
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about FAST TEXTURE INTRA SIZE CODING BASED ON BIG DATA CLUSTERING FOR 3D-HEVC
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Speaker Diarization with LSTM
- Log in to post comments
For many years, i-vector based audio embedding techniques were the dominant approach for speaker verification and speaker diarization applications. However, mirroring the rise of deep learning in various domains, neural network based audio embeddings, also known as d-vectors, have consistently demonstrated superior speaker verification performance. In this paper, we build on the success of d-vector based speaker verification systems to develop a new d-vector based approach to speaker diarization.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views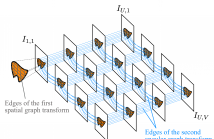
- Read more about GRAPH-BASED TRANSFORMS FOR PREDICTIVE LIGHT FIELD COMPRESSION BASED ON SUPER-PIXELS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we explore the use of graph-basedtransforms to capture correlation in light fields. We consider a scheme in which view synthesis is used as a first step to exploit inter-view correlation. Local graph-based transforms (GT) are then considered for energy compaction of the residue signals. The structure of the local graphs is derived from a coherent super-pixel over-segmentation of the different views. The GT is computed and applied in a separable manner with a first spatial unweighted transform followed by an inter-view GT.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about PERCEPTUALLY MOTIVATED ANALYSIS OF NUMERICALLY SIMULATED HEAD-RELATED TRANSFER FUNCTIONS GENERATED BY VARIOUS 3D SURFACE SCANNING SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
Numerical simulations offer a feasible alternative to the direct acoustic measurement of individual head-related transfer functions (HRTFs). For the acquisition of high quality 3D surface scans, as required for these simulations, several approaches exist. In this paper, we systematically analyze the variations between different approaches and evaluate the influence of the accuracy of 3D scans on the resulting simulated HRTFs. To assess this effect, HRTFs were numerically simulated based on 3D scans of the head and pinna of the FABIAN dummy head generated with 6 different methods.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views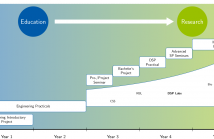
- Read more about Hands-on in Signal Processing Education at Technische Universität Darmstadt
- Log in to post comments
This paper is meant to share our experience on signal processing hands-on opportunities within the formal engineering education at Technische Universität Darmstadt. It is our strong belief that undergraduate students should be offered hands-on opportunities from the very beginning of their studies until their graduation. We describe our projects, lectures and seminars that we provide undergraduate students to gain hands-on experience inside signal processing along the time line of the curriculum.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
Combined PET-CT scan is an important diagnostic tool in modern medicine, e.g. for staging or treatment planning in the field of oncology. Especially in small structures, like a tumour, textural variations visible in a PET image are not visually recognizable within a CT scan from the same region. Thus, both modalities are necessary for diagnosis. Since both techniques expose the patient to radiation, it would be desirable to get the same information about metabolic activity contained in the PET image from a CT scan only.
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about ATTENTION-BASED MODELS FOR TEXT-DEPENDENT SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
Attention-based models have recently shown great performance on a range of tasks, such as speech recognition, machine translation, and image captioning due to their ability to summarize relevant information that expands through the entire length of an input sequence. In this paper, we analyze the usage of attention mechanisms to the problem of sequence summarization in our end-to-end text-dependent speaker recognition system. We explore different topologies and their variants of the attention layer, and compare different pooling methods on the attention weights.
- Categories:
 162 Views
162 Views
- Read more about Pattern Localization in Time Series through Signal-To-Model Alignment in Latent Space
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study the problem of locating a predefined sequence of patterns in a time series. In particular, the studied scenario assumes a theoretical model is available that contains the expected locations of the patterns. This problem is found in several contexts, and it is commonly solved by first synthesizing a time series from the model, and then aligning it to the true time series through dynamic time warping. We propose a technique that increases the similarity of both time series before aligning them, by mapping them into a latent correlation space.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Sparse overcomplete denoising: aggregation versus global optimization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views