
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about CNNs for Intra Prediction using Cross-Component Adaption - Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Presentation Slides for "Convolutional Neural Networks for Video Intra Prediction Using Cross-component Adaptation"
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views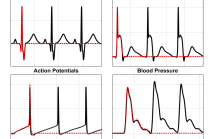
Modern medical science demands sophisticated signal representation methods in order to cope with the increasing amount of data. Important criteria for these methods are mainly low computational and storage costs, whereas the underlying mathematical model should still be interpretable and meaningful for the data analyst. One of the most promising models fulfilling these criteria is based on Hermite functions, however having some important limitations for specific biomedical wave shapes.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views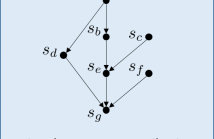
- Read more about A DISCRETE SIGNAL PROCESSING FRAMEWORK FOR MEET/JOIN LATTICES WITH APPLICATIONS TO HYPERGRAPHS AND TREES
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a novel discrete signal processing framework, called discrete-lattice SP, for signals indexed by a finite lattice. A lattice is a partially ordered set that supports a meet (or join) operation that returns the greatest element below two given elements. Discrete-lattice SP chooses the meet as shift operation and derives associated notion of (meet-invariant) convolution, Fourier transform, frequency response, and a convolution theorem. Examples of lattices include sets of sets that are closed under intersection and trees.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Poster - Acoustic Equalization for Headphones Using a Fixed Feed-Forward Filter
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about On the Sensitivity of Spectral Initialization for Noisy Phase Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
The spectral method is an important approach for signal esti- mation that is often used as an initialization to iterative methods as well as a stand-alone estimator, where the signal is estimated by the top eigenvector of certain carefully-constructed data matrix. A re- cent line of work has characterized the asymptotic behavior of such data matrices used in spectral methods, which reveals an interesting phase transition phenomenon: there exists a critical sampling thresh- old below which the estimate of the spectral method is uninforma- tive.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Solving Quadratic Equations via Amplitude-based Nonconvex Optimization
- Log in to post comments
In many signal processing tasks, one seeks to recover an r- column matrix object X ∈ Cn×r from a set of nonnegative quadratic measurements up to orthonormal transforms. Example applications include coherence retrieval in optical imaging and co- variance sketching for high-dimensional streaming data. To this end, efficient nonconvex optimization methods are quite appealing, due to their computational efficiency and scalability to large-scale problems.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Squared-Loss Mutual Information via High-Dimension Coherence Matrix Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Squared-loss mutual information (SMI) is a surrogate of Shannon mutual information that is more advantageous for estimation. On the other hand, the coherence matrix of a pair of random vectors, a power-normalized version of the sample cross-covariance matrix, is a well-known second-order statistic found in the core of fundamental signal processing problems, such as canonical correlation analysis (CCA).
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about MSE Based Precoding Schemes For Partially Correlated Transmissions In Interference Channels
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider interference channel model in which transmissions from multiple users are partially correlated. This correlation arises in wireless sensor network (WSN) scenarios and temporally correlated models. Considering this model, two minimum mean squared error (MSE) based precoding methods are derived. With these formulations, an iterative convergent procedure is formulated similar to a typical interference alignment (IA) algorithm. Simulations show that the second method provides the best sum rates for different correlation values.
poster2.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Content Placement Learning For Success Probability Maximization In Wireless Edge Caching Networks
- Log in to post comments
To meet increasing demands of wireless multimedia communications, caching of important contents in advance is one of the key solutions. Optimal caching depends on content popularity in future which is unknown in advance. In this paper, modeling content popularity as a finite state Markov chain, reinforcement Q-learning is employed to learn optimal content placement strategy in homogeneous Poisson point process (PPP) distributed caching network.
posterq2.pdf
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Feedforward Spatial Active Noise Control Based on Kernel Interpolation of Sound Field
- Log in to post comments
A method for feedforward active noise control (ANC) over a spatial region is proposed. Conventional multipoint ANC aims to reduce the noise at multiple discrete positions; therefore, the noise reduction in the region between these points cannot be guaranteed. Recent studies revealed the possibility of spatial ANC, i.e., noise control in a continuous target region.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views