
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2020 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Experiments in Creating Online Course Content for Signal Processing Education
- Log in to post comments
A brief introduction to the NPTEL.ac.in platform of India which
provides free access to quality online educational content for
Signal Processing. Experiences of creating courses related to Signal Processing,
supported by the European Union-funded project, MIELES.
- Categories:
 85 Views
85 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Networks for Secure Wireless Communications - Slides
- Log in to post comments
We propose a data-driven secure wireless communication scheme, in which the goal is to transmit a signal to a legitimate receiver with minimal distortion, while keeping some information about the signal private from an eavesdropping adversary. When the data distribution is known, the optimal trade-off between the reconstruction quality at the legitimate receiver and the leakage to the adversary can be characterised in the information theoretic asymptotic limit.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about UNIFIED SIGNAL COMPRESSION USING GENERATIVE ADVERSARIAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a unified compression framework that uses generative adversarial networks (GAN) to compress image and speech signals. The compressed signal is represented by a latent vector fed into a generator network which is trained to produce high-quality signals that minimize a target objective function. To efficiently quantize the compressed signal, non-uniformly quantized optimal latent vectors are identified by iterative back-propagation with ADMM optimization performed for each iteration.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views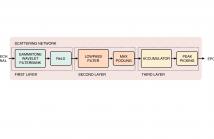
- Read more about EPOCH EXTRACTION FROM A SPEECH SIGNAL USING GAMMATONE WAVELETS IN A SCATTERING NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
In speech production, epochs are glottal closure instants where significant energy is released from the lungs. Extracting an epoch accurately is important in speech synthesis, analysis, and pitch oriented studies. The time-varying characteristics of the source and the system, and channel attenuation of low-frequency components by telephone channels make estimation of epoch from a speech signal a challenging task.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about Embedded Large–Scale Handwritten Chinese Character Recognition
- Log in to post comments
As handwriting input becomes more prevalent, the large symbol inventory required to support Chinese handwriting recognition poses unique challenges. This paper describes how the Apple deep learning recognition system can accurately handle up to 30,000 Chinese characters while running in real-time across a range of mobile devices.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about MULTI-LABEL CONSISTENT CONVOLUTIONAL TRANSFORM LEARNING: APPLICATION TO NON-INTRUSIVE LOAD MONITORING
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
- Read more about Automatic identification of speakers from head gestures in a narration
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we focus on quantifying speaker identity information encoded in the head gestures of speakers, while they narrate a story. We hypothesize that the head gestures over a long duration have speaker-specific patterns. To establish this, we consider a classification problem to identify speakers from head gestures. We represent every head orientation as a triplet of Euler angles and a sequence of head orientations as head gestures.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about Multi-scale Octave Convolutions for Robust Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We propose a multi-scale octave convolution layer to learn robust speech representations efficiently. Octave convolutions were introduced by Chen et al [1] in the computer vision field to reduce the spatial redundancy of the feature maps by decomposing the output of a convolutional layer into feature maps at two different spatial resolutions, one octave apart. This approach improved the efficiency as well as the accuracy of the CNN models. The accuracy gain was attributed to the enlargement of the receptive field in the original input space.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about PORTFOLIO CUTS: A GRAPH-THEORETIC FRAMEWORK TO DIVERSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views