
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
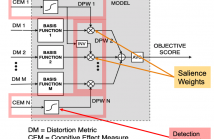
- Read more about A Data-driven Cognitive Salience Model for Objective Perceptual Audio Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Objective audio quality assessment systems often use perceptual models to predict the subjective quality scores of processed signals, as reported in listening tests. Most systems map different metrics of perceived degradation into a single quality score predicting subjective quality. This requires a quality mapping stage that is informed by real listening test data using statistical learning (\iec a data-driven approach) with distortion metrics as input features.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about FAST-RIR: FAST NEURAL DIFFUSE ROOM IMPULSE RESPONSE GENERATOR
- Log in to post comments
We present a neural-network-based fast diffuse room impulse response generator (FAST-RIR) for generating room impulse responses (RIRs) for a given acoustic environment. Our FAST-RIR takes rectangular room dimensions, listener and speaker positions, and reverberation time as inputs and generates specular and diffuse reflections for a given acoustic environment. Our FAST-RIR is capable of generating RIRs for a given input reverberation time with an average error of 0.02s.
- Categories:
 71 Views
71 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED DEEP LEARNING NETWORK FOR DEFORMABLE FUNDUS IMAGE REGISTRATION
- Log in to post comments
In ophthalmology and vision science applications, the process of registering a pair of fundus images, captured at different scales and viewing angles, is of paramount importance to support the diagnosis of diseases and routine eye examinations. Aiming at addressing the retina registration problem from the Deep Learning perspective, in this paper we introduce an end-to-end framework capable of learning the registration task in a fully unsupervised way.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views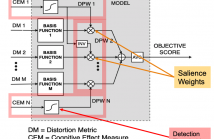
- Read more about A Data-Driven Cognitive Salience Model for Objective Perceptual Audio Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Objective audio quality assessment systems often use perceptual models to predict the subjective quality scores of processed signals, as reported in listening tests. Most systems map different metrics of perceived degradation into a single quality score predicting subjective quality. This requires a quality mapping stage that is informed by real listening test data using statistical learning (\iec a data-driven approach) with distortion metrics as input features.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views

- Read more about Panchromatic imagery copy-paste localization through data-driven sensor attribution
- Log in to post comments
Overhead images can be obtained using different acquisition and processing techniques, and they are becoming more and more popular. As with common photographs, they can be forged and manipulated by malicious users. However, not all image forensics methods tailored to normal photos can be successfully applied out of the box to overhead images. In this paper we consider the problem of localizing copy-paste forgeries on panchromatic images acquired with different satellites.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about COMBINING MULTIPLE STYLE TRANSFER NETWORKS AND TRANSFER LEARNING FOR LGE-CMR SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views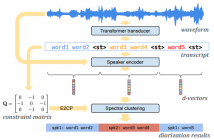
- Read more about Turn-to-Diarize: Online Speaker Diarization Constrained by Transformer Transducer Speaker Turn Detection
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a novel speaker diarization system for streaming on-device applications. In this system, we use a transformer transducer to detect the speaker turns, represent each speaker turn by a speaker embedding, then cluster these embeddings with constraints from the detected speaker turns. Compared with conventional clustering-based diarization systems, our system largely reduces the computational cost of clustering due to the sparsity of speaker turns.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Actor-Critic Bilateral Filter
- Log in to post comments
Recent research on edge-preserving image smoothing has suggested that bilateral filtering is vulnerable to maliciously perturbed filtering input. However, while most prior works analyze the adaptation of the range kernel in one-step manner, in this paper we take a more constructive view towards multi-step framework with the goal of unveiling the vulnerability of bilateral filtering.
Paper1162_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 59 Views
59 Views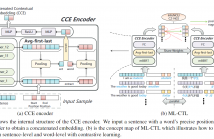
- Read more about MULTI-LEVEL CONTRASTIVE LEARNING FOR CROSS-LINGUAL ALIGNMENT
- Log in to post comments
Cross-language pre-trained models such as multilingual BERT (mBERT) have achieved significant performance in various cross-lingual downstream NLP tasks. This paper proposes a multi-level contrastive learning (ML-CTL) framework to further improve the cross-lingual ability of pre-trained models. The proposed method uses translated parallel data to encourage the model to generate similar semantic embeddings for different languages.
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views