
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
- Read more about AN INVESTIGATION OF THE EFFECTIVENESS OF PHASE FOR AUDIO CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
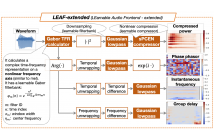
While log-amplitude mel-spectrogram has widely been used as the feature representation for processing speech based on deep learning, the effectiveness of another aspect of speech spectrum, i.e., phase information, was shown recently for tasks such as speech enhancement and source separation. In this study, we extensively investigated the effectiveness of including phase information of signals for eight audio classification tasks. We constructed a learnable front-end that can compute the phase and its derivatives based on a time-frequency representation with mel-like frequency axis.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about ADT: ANTI-DEEPFAKE TRANSFORMER
- Log in to post comments
Recently almost all the mainstream deepfake detection methods use Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) as their backbone. However, due to the overreliance on local texture information, which is usually determined by forgery methods of training data, these CNN based methods cannot generalize well to unseen data. To get out of the predicament of prior methods, in this paper, we propose a novel transformer-based framework to model both global and local information and analyze anomalies of face images.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Region-to-region kernel interpolation of acoustic transfer function with directional weighting
- Log in to post comments
A method of interpolating the acoustic transfer function (ATF) between regions that takes into account both the physical properties of the ATF and the directionality of region configurations is proposed. Most spatial ATF interpolation methods are limited to estimation in the region of receivers. A kernel method for region-to-region ATF interpolation makes it possible to estimate the ATFs for both source and receiver regions from a discrete set of ATF measurements.
- Categories:
 81 Views
81 Views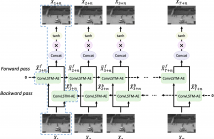
- Read more about Video Anomaly Detection via Prediction Network with Enhanced Spatio-temporal Memory Exchange
- Log in to post comments
Video anomaly detection is a challenging task because most anomalies are scarce and non-deterministic. Many approaches investigate the reconstruction difference between normal and abnormal patterns, but neglect that anomalies do not necessarily correspond to large reconstruction errors. To address this issue, we design a Convolutional LSTM Auto-Encoder prediction framework with enhanced spatio-temporal memory exchange using bi-directionalilty and a higher-order mechanism. The bi-directional structure promotes learning the temporal regularity through forward and backward predictions.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views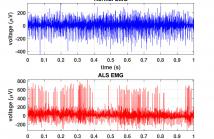
- Read more about ALSNET: A DILATED 1-D CNN FOR IDENTIFYING ALS FROM RAW EMG SIGNAL (Presentation Slides)
- Log in to post comments
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most common neuromuscular diseases which affects both lower and upper motor neurons. In this paper, a dilated one dimensional convolutional neural network, named ALSNet, is proposed for identifying ALS from raw EMG signal. No hand-crafted feature extraction is required, rather, ALSNet is able to take raw EMG signal as input and detect EMG signals of ALS subjects. This makes the method more feasible for practical implementation by reducing the computational cost required for extracting features.
- Categories:
 523 Views
523 Views
- Read more about LOOK, LISTEN AND PAY MORE ATTENTION: FUSING MULTI-MODAL INFORMATION FOR VIDEO VIOLENCE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Violence detection is an essential and challenging problem in the computer vision community. Most existing works focus on single modal data analysis, which is not effective when multi-modality is available.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views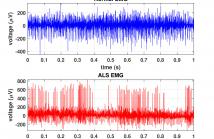
- Read more about ALSNET: A DILATED 1-D CNN FOR IDENTIFYING ALS FROM RAW EMG SIGNAL (Poster)
- Log in to post comments
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is one of the most common neuromuscular diseases which affects both lower and upper motor neurons. In this paper, a dilated one dimensional convolutional neural network, named ALSNet, is proposed for identifying ALS from raw EMG signal. No hand-crafted feature extraction is required, rather, ALSNet is able to take raw EMG signal as input and detect EMG signals of ALS subjects. This makes the method more feasible for practical implementation by reducing the computational cost required for extracting features.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views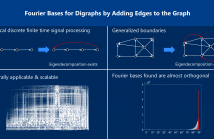
- Read more about Digraph Signal Processing with Generalized Boundary Conditions
- Log in to post comments
Signal processing on directed graphs (digraphs) is problematic, since the graph shift, and thus associated filters, are in general not diagonalizable. Furthermore, the Fourier transform in this case is now obtained from the Jordan decomposition, which may not be computable at all for large graphs. We propose a novel and general solution for this problem based on matrix perturbation theory: We design an algorithm that adds a small number of edges to a given digraph to destroy nontrivial Jordan blocks.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
Few-shot segmentation has got a lot of concerns recently. Existing methods mainly locate and recognize the target object based on a cross-guided way that applies masked target object features of sup- port(query) images to make a feature matching with query(support) images. However, there are some differences between support images and query images because of large appearance and scale variation, which will lead to inaccurate and incomplete segmentation. This problem inspired us to explore the local coherence of the image to guide the segmentation.
icassp.pptx
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views