
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Robust Recovery of Jointly-Sparse Signals Using Minimax Concave Loss Function
- Log in to post comments
We propose a robust approach to recovering jointly sparse signals in the presence of outliers. The robust recovery task is cast as a convex optimization problem involving a minimax concave loss function (which is weakly convex) and a strongly convex regularizer (which ensures the overall convexity). The use of the nonconvex loss makes the problem difficult to solve directly by the convex optimization methods even with the well-established firm shrinkage.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about A QUESTION-ORIENTED PROPAGATION NETWORK FOR NEWS READING COMPREHENSION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views
The projection of sample measurements onto a reconstruction space represented by a basis on a regular grid is a powerful and simple approach to estimate a probability density function. In this paper, we focus on Riesz bases and propose a projection operator that, in contrast to previous works, guarantees the bona fide properties for the estimate, namely, non-negativity and total probability mass 1. Our bona fide projection is defined as a convex problem. We propose solution techniques and evaluate them.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Bona fide Riesz projections for density estimation - Presentation
- Log in to post comments
The projection of sample measurements onto a reconstruction space represented by a basis on a regular grid is a powerful and simple approach to estimate a probability density function. In this paper, we focus on Riesz bases and propose a projection operator that, in contrast to previous works, guarantees the bona fide properties for the estimate, namely, non-negativity and total probability mass 1. Our bona fide projection is defined as a convex problem. We propose solution techniques and evaluate them.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Robust Unstructured Knowledge Access In Conversational Dialogue With ASR Errors
- Log in to post comments
Performance of spoken language understanding (SLU) can be degraded with automatic speech recognition (ASR) errors. We propose a novel approach to improve SLU robustness by randomly corrupting clean training text with an ASR error simulator, followed by self-correcting the errors and minimizing the target classification loss in a joint manner. In the proposed error simulator, we leverage confusion networks generated from an ASR decoder without human transcriptions to generate variety of error patterns for model training.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Fast learning of fast transforms, with guarantees (ICASSP 2022 video)
- Log in to post comments
Approximating a matrix by a product of few sparse factors whose supports possess the butterfly structure, which is common to many fast transforms, is key to learn fast transforms and speed up algorithms for inverse problems. We introduce a hierarchical approach that recursively factorizes the considered matrix into two factors. Using recent advances on the well-posedness and tractability of the two-factor fixed-support sparse matrix factorization problem, the proposed algorithm is endowed with exact recovery guarantees.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views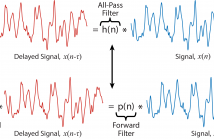
- Read more about An Adaptive All-Pass Filter for Time-Varying Delay Estimation
- Log in to post comments
The focus of this paper is the estimation of a delay between two signals. Such a problem is common in signal processing and particularly challenging when the delay is nonstationary in nature. Our proposed solution is based on an allpass filter framework comprising of two elements: a time delay is equivalent to all-pass filtering and an all-pass filter can be represented in terms of a ratio of a finite impulse response (FIR) filter and its time reversal.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about ON SYNCHRONIZATION OF WIRELESS ACOUSTIC SENSOR NETWORKS IN THE PRESENCE OF TIME-VARYING SAMPLING RATE OFFSETS AND SPEAKER CHANGES
- Log in to post comments
poster_landscape.pdf
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Learning task-specific representation for Video anomaly detection with spatial-temporal attention
- Log in to post comments
The automatic detection of abnormal events in surveillance videos with weak supervision has been formulated as a multiple instance learning task, which aims to localize the clips containing abnormal events temporally with the video-level labels. However, most existing methods rely on the features extracted by the pre-trained action recognition models, which are not discriminative enough for video anomaly detection.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views