
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Zero Resource Code-switched Speech Benchmark Using Speech Utterance Pairs For Multiple Spoken Languages
- Log in to post comments
We introduce a new zero resource code-switched speech benchmark designed to directly assess the code-switching capabilities of self-supervised speech encoders. We showcase a baseline system of language modeling on discrete units to demonstrate how the code-switching abilities of speech encoders can be assessed in a zero-resource manner. Our experiments encompass a variety of well-known speech encoders, including Wav2vec 2.0, HuBERT, XLSR, etc. We examine the impact of pre-training languages and model size on benchmark performance.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about Hyperspectral Image Reconstruction using Hierarchical Neural Architecture Search from a Snapshot Image
- Log in to post comments
Hyperspectral imaging is a promising imaging modality, and has attracted increasing research attention by compressive sensing such as coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging (CASSI), for simultaneously capturing abundant information in spatial, spectral and temporal domains. Hyperspectral image (HSI) reconstruction in the CASSI aims to retrieve the original 3D signal upon the 2D compressed snapshot.
ID6267.pdf
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views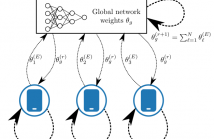
- Read more about Federated Dataset Dictionary Learning For Multi-Source Domain Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
In this article, we propose an approach for federated domain adaptation, a setting where distributional shift exists among clients and some have unlabeled data. The proposed framework, FedDaDiL, tackles the resulting challenge through dictionary learning of empirical distributions. In our setting, clients' distributions represent particular domains, and FedDaDiL collectively trains a federated dictionary of empirical distributions. In particular, we build upon the Dataset Dictionary Learning framework by designing collaborative communication protocols and aggregation operations.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about Deep Versatile Hyperspectral Reconstruction Model from a Snapshot Measurement with Arbitrary Masks
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Recently, coded aperture snapshot spectral imaging (CASSI) has been actively researched to capture three-dimensional (3D) hyperspectral (HS) images for dynamic scenes, where the optical systems detect a 2D snapshot measurement while a computational algorithm performs the inverse problem for recovering the latent HS cubic data. Benefiting from the powerful modeling capability of the deep convolution neural networks (DCNN), the reconstruction performance of the HS images has been significantly improved.
ID1717.pdf
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views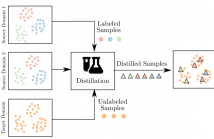
- Read more about Multi-Source Domain Adaptation meets Dataset Distillation through Dataset Dictionary Learning
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we consider the intersection of two problems in machine learning: Multi-Source Domain Adaptation (MSDA) and Dataset Distillation (DD). On the one hand, the first considers adapting multiple heterogeneous labeled source domains to an unlabeled target domain. On the other hand, the second attacks the problem of synthesizing a small summary containing all the information about the datasets. We thus consider a new problem called MSDA-DD.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views- Read more about Multi-Level Graph Learning For Audio Event Classification And Human-Perceived Annoyance Rating Prediction
- Log in to post comments
WHO's report on environmental noise estimates that 22 M people suffer from chronic annoyance related to noise caused by audio events (AEs) from various sources. Annoyance may lead to health issues and adverse effects on metabolic and cognitive systems. In cities, monitoring noise levels does not provide insights into noticeable AEs, let alone their relations to annoyance. To create annoyance-related monitoring, this paper proposes a graph-based model to identify AEs in a soundscape, and explore relations between diverse AEs and human-perceived annoyance rating (AR).
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about A SALIENCY ENHANCED FEATURE FUSION BASED MULTISCALE RGB-D SALIENT OBJECT DETECTION NETWORK
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Multiscale convolutional neural network (CNN) has demonstrated remarkable capabilities in solving various vision problems. However, fusing features of different scales always results in large model sizes, impeding the application of mul-
tiscale CNNs in RGB-D saliency detection. In this paper, we propose a customized feature fusion module, called Saliency Enhanced Feature Fusion (SEFF), for RGB-D saliency detection. SEFF utilizes saliency maps of the neighboring scales
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Image Mixing and Gradient Smoothing to Enhance the SAR Image Attack
- Log in to post comments
Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are known to be vulnerable to adversarial examples, which are crafted by adding imperceptible perturbations to clean examples. With the wide applications of DNNs to Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) Automatic Target Recognition (ATR), the vulnerability of SAR deep recognition models has attracted increasing attention.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have been considered recently for target localization. While existing literature typically uses fixed RISs in the environment, mounting RISs on targets is a novel approach that can improve target visibility and positioning. This study derives the Cramér-Rao bound (CRB) for pose estimation (i.e., RIS position and orientation) under a generic wideband and near-field model. The theoretical findings show that a pose-dependent filtering phenomenon occurs, impacting the CRB, which is neglected under narrowband approximation.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about DIFFUSION-BASED SPEECH ENHANCEMENT WITH JOINT GENERATIVE AND PREDICTIVE DECODERS
- Log in to post comments
Diffusion-based generative speech enhancement (SE) has recently received attention, but reverse diffusion remains time-consuming. One solution is to initialize the reverse diffusion process with enhanced features estimated by a predictive SE system. However, the pipeline structure currently does not consider for a combined use of generative and predictive decoders. The predictive decoder allows us to use the further complementarity between predictive and diffusion-based generative SE.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views