
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about Poster of the paper "Multivariate Density Estimation Using Low-Rank Fejér-Riesz Factorization"
- Log in to post comments
We consider the problem of learning smooth multivariate probability density functions. We invoke the canonical decomposition of multivariate functions and we show that if a joint probability density function admits a truncated Fourier series representation, then the classical univariate Fejér-Riesz Representation Theorem can be used for learning bona fide joint probability density functions. We propose a scalable, flexible, and direct framework for learning smooth multivariate probability density functions even from potentially incomplete datasets.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
- Read more about Improving Continual Learning of Acoustic Scene Classification via Mutual Information Optimization
- Log in to post comments
Continual learning, which aims to incrementally accumulate knowledge, has been an increasingly significant but challenging research topic for deep models that are prone to catastrophic forgetting. In this paper, we propose a novel replay-based continual learning approach in the context of class-incremental learning in acoustic scene classification, to classify audio recordings into an expanding set of classes that characterize the acoustic scenes. Our approach is improving both the modeling and memory selection mechanism via mutual information optimization in continual learning.
MIO_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Low-bitrate redundancy coding of speech for packet loss concealment in teleconferencing
- Log in to post comments
conferencing applications. We introduced a novel neural codec for low-bitrate speech coding at 6 kbit/s, with long 1 kbit/s redundancy, that also enhances speech by suppressing noise and reverberation. Transmitting large amounts of redundant information allows for speech reconstruction on the receiver side during severe packet loss – see ICASSP paper ID 7175: “Ultra low bitrate loss resilient neural speech enhancing codec”.
- Categories:
 72 Views
72 Views
- Read more about EARLY DIAGNOSING PARKINSON'S DISEASE VIA A DEEP LEARNING MODEL BASED ON AUGMENTED FACIAL EXPRESSION DATA
- Log in to post comments
It is crucial to promptly diagnose potential Parkinson's disease (PD) patients in order to facilitate early treatment and prevent disease progression. In recent years, there has been growing interest in using facial expressions for in-vitro PD diagnosis due to the distinct "masked face" characteristics of PD patients and the cost-effectiveness of this approach. However, current facial expression-based PD diagnosis methods are hindered by limited training data on PD patients' facial expressions and weak prediction models.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views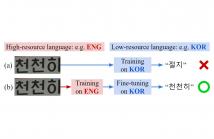
- Read more about CROSS-LINGUAL LEARNING IN MULTILINGUAL SCENE TEXT RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we investigate cross-lingual learning (CLL) for multilingual scene text recognition (STR). CLL transfers knowledge from one language to another. We aim to find the condition that exploits knowledge from high-resource languages for improving performance in low-resource languages. To do so, we first examine if two general insights about CLL discussed in previous works are applied to multilingual STR: (1) Joint learning with high- and low-resource languages may reduce performance on low-resource languages, and (2) CLL works best between typologically similar languages.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Estimating exercise-induced fatigue from thermal facial images
- Log in to post comments
Exercise-induced fatigue resulting from physical activity can
be an early indicator of overtraining, illness, or other health
issues. In this article, we present an automated method for
estimating exercise-induced fatigue levels through the use of
thermal imaging and facial analysis techniques utilizing deep
learning models. Leveraging a novel dataset comprising over
400,000 thermal facial images of rested and fatigued users,
our results suggest that exercise-induced fatigue levels could
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Debris sensing based on LEO constellation: an intersatellite channel parameter estimation approach
- Log in to post comments
Space debris detection and tracking, a key enabler for Space Situational Awareness (SSA), poses two inherent challenges: (1) small-sized targets (e.g., $1-10~cm$) posing detection difficulties for conventional ground-based radars (GBRs) and optical measurements; (2) large number resulting in a costly tracking exercise. To address these, this work utilizes intersatellite link (ISL) in the emerging low earth orbit (LEO) constellations to opportunistically sense debris. The spatially dense-distributed debris is modeled as a cluster to reduce the number of quantities estimated.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about ECM-OPCC: Efficient Context Model for Octree-based Point Cloud Compression
- Log in to post comments
Recently, deep learning methods have shown promising results in point cloud compression. However, previous octree-based approaches either lack sufficient context or have high decoding complexity (e.g. > 900s). To address this problem, we propose a sufficient yet efficient context model and design an efficient deep learning codec for point clouds. Specifically, we first propose a segment-constrained multi-group coding strategy to exploit the autoregressive context while maintaining decoding efficiency.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about GENEFORMER: LEARNED GENE COMPRESSION USING TRANSFORMER-BASED CONTEXT MODELING
- Log in to post comments
The development of gene sequencing technology sparks an explosive growth of gene data. Thus, the storage of gene data has become an important issue. Recently, researchers begin to investigate deep learning-based gene data compression, which outperforms general traditional methods. In this paper, we propose a transformer-based gene compression method named GeneFormer. Specifically, we first introduce a modified transformer encoder with latent array to eliminate the dependency of the nucleotide sequence.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
Modern social media platforms play an important role in facilitating rapid dissemination of information through their massive user networks. Fake news, misinformation, and unverifiable facts on social media platforms propagate disharmony and affect society. In this paper, we consider the problem of misinformation detection which classify news items as fake or real. Specifically, driven by experiential studies on real-world social media platforms, we propose a probabilistic Markovian information spread model over networks modeled by graphs.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views