
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

Federated learning is a technique that allows multiple entities to collaboratively train models using their data without compromising data privacy. However, despite its advantages, federated learning can be susceptible to false data injection attacks. In these scenarios, a malicious entity with control over specific agents in the network can manipulate the learning process, leading to a suboptimal model. Consequently, addressing these data injection attacks presents a significant research challenge in federated learning systems.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about BigVSAN: Enhancing GAN-based Neural Vocoders with Slicing Adversarial Network
- Log in to post comments
Generative adversarial network (GAN)-based vocoders have been intensively studied because they can synthesize high-fidelity audio waveforms faster than real-time. However, it has been reported that most GANs fail to obtain the optimal projection for discriminating between real and fake data in the feature space. In the literature, it has been demonstrated that slicing adversarial network (SAN), an improved GAN training framework that can find the optimal projection, is effective in the image generation task. In this paper, we investigate the effectiveness of SAN in the vocoding task.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about MULTIMODAL IMAGING FEATURE EXTRACTION WITH REFERENCE CANONICAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS UNDERLYING INTELLIGENCE
- Log in to post comments
With neuroimaging data scientists have gained substantial information on the neuronal underpinning of intelligence. Yet how to integrate multimodal neuronal features effectively in relation to intelligence remains elusive. In this paper, we have developed a reference Canonical Correlation Analysis (RCCA) model that extracts latent, correlated multimodal features while enhancing correlation to a reference of interest.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views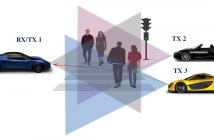
- Read more about Space-Time Adaptive Processing for radars in Connected and Automated Vehicular Platoons
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we develop a holistic framework for space-time adaptive processing (STAP) in connected and automated vehicle (CAV) radar systems. We investigate a CAV system consisting of multiple vehicles that transmit frequency-modulated continuous-waveforms (FMCW), thereby functioning as a multistatic radar. Direct application of STAP in a network of radar systems such as in a CAV may lead to excess interference. We exploit time division multiplexing (TDM) to perform transmitter scheduling over FMCW pulses to achieve high detection performance.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about NEURAL NETWORK-BASED SYMBOLIC REGRESSION FOR EMPIRICAL MODELING OF THE BEHAVIOR OF A PLANETARY GEARBOX
- Log in to post comments
Gearbox condition monitoring and quality surveillance are crucial techniques to ensure safe and cost-efficient machine operations. In condition monitoring, the interpretation of the different vibration spectrum elements is still an open question, many works show that some predefined vibration models are improper to explain the spectrum contents. In this paper, we investigate a method to identify the mixture model that describes a single-stage planetary gearbox vibration to properly interpret the vibration spectrum.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views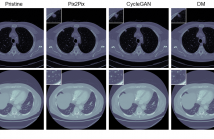
- Read more about M3DSYNTH: A DATASET OF MEDICAL 3D IMAGES WITH AI-GENERATED LOCAL MANIPULATIONS
- Log in to post comments
The ability to detect manipulated visual content is becoming increasingly important in many application fields, given the rapid advances in image synthesis methods. Of particular concern is the possibility of modifying the content of medical images, altering the resulting diagnoses. Despite its relevance, this issue has received limited attention from the research community. One reason is the lack of large and curated datasets to use for development and benchmarking purposes.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Source-Free Online Domain Adaptive Semantic Segmentation of Satellite Images under Image Degradation
- Log in to post comments
Online adaptation to distribution shifts in satellite image segmentation stands as a crucial yet underexplored problem. In this paper, we address source-free and online domain adaptation, i.e., test-time adaptation (TTA), for satellite images, with the focus on mitigating distribution shifts caused by various forms of image degradation. Towards achieving this goal, we propose a novel TTA approach involving two effective strategies. First, we progressively estimate the global Batch Normalization (BN) statistics of the target distribution with incoming data stream.
ICASSP_24__final.pdf
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about Spatial Scaper: A Library to Simulate and Augment Soundscapes for Sound Event Localization and Detection in Realistic Rooms
- Log in to post comments
Sound event localization and detection (SELD) is an important task in machine listening.
Major advancements rely on simulated data with sound events in specific rooms and strong spatio-temporal labels.
SELD data is simulated by convolving spatialy-localized room impulse responses (RIRs) with sound waveforms to place sound events in a soundscape.
However, RIRs require manual collection in specific rooms.
We present SpatialScaper, a library for SELD data simulation and augmentation.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about PROMPTING AUDIOS USING ACOUSTIC PROPERTIES FOR EMOTION REPRESENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Emotions lie on a continuum, but current models treat emotions
as a finite valued discrete variable. This representation does not
capture the diversity in the expression of emotion. To better rep-
resent emotions we propose the use of natural language descrip-
tions (or prompts). In this work, we address the challenge of au-
tomatically generating these prompts and training a model to better
learn emotion representations from audio and prompt pairs. We use
acoustic properties that are correlated to emotion like pitch, intensity,
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Virtual Bass Enhancement via Music Demixing
- Log in to post comments
Virtual Bass Enhancement (VBE) refers to a class of digital signal processing algorithms that aim at enhancing the perception of low frequencies in audio applications. Such algorithms typically exploit well-known psychoacoustic effects and are particularly valuable for improving the performance of small-size transducers often found in consumer electronics. Though both time- and frequency-domain techniques have been proposed in the literature, none of them capitalizes on the latest achievements of deep learning as far as music processing is concerned.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views