
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about PROMPTING LARGE LANGUAGE MODELS WITH FINE-GRAINED VISUAL RELATIONS FROM SCENE GRAPH FOR VISUAL QUESTION ANSWERING
- Log in to post comments
Visual Question Answering (VQA) is a task that requires models to comprehend both questions and images. An increasing number of works are leveraging the strong reasoning capabilities of Large Language Models (LLMs) to address VQA. These methods typically utilize image captions as visual text description to aid LLMs in comprehending images. However, these captions often overlooking the relations of fine-grained objects, which will limit the reasoning capability of LLMs. In this paper, we present PFVR, a modular framework that Prompts LLMs with Fine-grained Visual Relationships for VQA.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
- Read more about ESVC: Combining Adaptive Style Fusion and Multi-Level Feature Disentanglement for Expressive Singing Voice Conversion
- Log in to post comments
Nowadays, singing voice conversion (SVC) has made great strides in both naturalness and similarity for common SVC with a neutral expression. However, besides singer identity, emotional expression is also essential to convey the singer's emotions and attitudes, but current SVC systems can not effectively support it. In this paper, we propose an expressive SVC framework called ESVC, which can convert singer identity and emotional style simultaneously.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views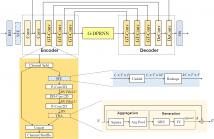
- Read more about GTCRN: A Speech Enhancement Model Requiring Ultralow Computational Resources
- Log in to post comments
While modern deep learning-based models have significantly outperformed traditional methods in the area of speech enhancement, they often necessitate a lot of parameters and extensive computational power, making them impractical to be deployed on edge devices in real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce Grouped Temporal Convolutional Recurrent Network (GTCRN), which incorporates grouped strategies to efficiently simplify a competitive model, DPCRN. Additionally, it leverages subband feature extraction modules and temporal recurrent attention modules to enhance its performance.
GTCRN_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 304 Views
304 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Continual Learning to Transfer Self-Supervised Speech Representations for Voice Pathology Detection
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, voice pathology detection (VPD) has received considerable attention because of the increasing risk of voice problems. Several methods, such as support vector machine and convolutional neural network-based models, achieve good VPD performance. To further improve the performance, we use a self-supervised pretrained model as feature representation instead of explicit speech features. When the pretrained model is fine-tuned for VPD, an overfitting problem occurs due to a domain shift from conversation speech to the VPD task.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Visualization of SLAM Backend Accelerator
- Log in to post comments
This research aims to develop energy-efficient hardware accelerators for Simultaneous Location And Mapping (SLAM) back end applications by employing algorithm-hardware co-design. Utilizing the iSAM2 algorithm, which uses graphical modeling to solve iterative Gauss-Newton problems, we continuously update maps by incorporating solutions from previous iterations or timesteps. We address the performance bottleneck arising from memory writes of intermediate results by modifying the original algorithm. Additionally, we analyze the algorithm's parallelizability to meet latency demands.
Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views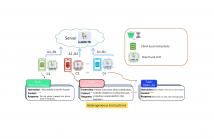
- Read more about Towards Building the Federated GPT: Federated Instruction Tuning
- Log in to post comments
While "instruction-tuned" generative large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated an impressive ability to generalize to new tasks, the training phases heavily rely on large amounts of diverse and high-quality instruction data (such as ChatGPT and GPT-4). Unfortunately, acquiring high-quality instructions, especially when it comes to human-written instructions, can pose significant challenges both in terms of cost and accessibility. Moreover, concerns related to privacy can further limit access to such data, making the process of obtaining it a complex and nuanced undertaking.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
- Read more about UAV OPERATION TIME MINIMIZATION FOR WIRELESS-POWERED DATA COLLECTION
- Log in to post comments
Employing unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) for data collection is crucial in facilitating autonomous monitoring applications within wireless sensor networks (WSNs). To enable sustainable WSNs, wireless powering of ground nodes (GNs) from a flying UAV is a promising technique. However, to maximize utility, we need to smartly allocate the limited resources of UAVs. To this end, we propose jointly optimizing the UAV’s trajectory and time allocation per GN to reduce operation time.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Tag Antenna Structure Calibrated Backscattering Signal Detection
- Log in to post comments
Backscatter Communication (BackCom) is gaining popularity due to its potential for sustainable and low-cost Internet of Things (IoT) applications. However, due to the limited resources of passive tags, optimizing the backscatter modulation is critical for the widespread use of this technology. Current backscatter modulation designs ignore the impact of the tag’s antenna structure, which we show in this paper to have a negative effect on system performance and lead to design discrepancies.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about RADAR PERCEPTION WITH SCALABLE CONNECTIVE TEMPORAL RELATIONS FOR AUTONOMOUS DRIVING
- Log in to post comments
Due to the noise and low spatial resolution in automotive radar data, exploring temporal relations of learnable features over consecutive 2 radar frames has shown performance gain on downstream tasks (e.g., object detection and tracking) in our previous study. In this paper, we further enhance radar perception by significantly extending the time horizon of temporal relations.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Secure Energy Efficiency Fairness Maximization in Backscatter Throughput Constrained UAV-assisted Data Collection
- Log in to post comments
Collecting reliable data over extended areas in rural environments for surveillance purposes requires low-cost and effective technologies. This paper proposes a backscattering data collection system that uses unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) to overcome wireless coverage challenges in rural areas. The proposed system provides physical layer security during autonomous data collection, and we optimize the UAV’s trajectory to manage data leakage while taking into account the limited battery of the UAV.
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views