
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
- Read more about Global Convergence of Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers for Invex Objective Losses
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
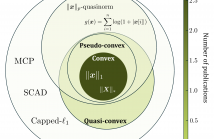
The Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers (ADMM) is uniquely suited for large-scale signal restoration problems, owing to its parallelizability. ADMM has been successfully deployed into several imaging modalities, including blind ptychography, phase retrieval, computer tomography, network unrolling, and magnetic resonance imaging. It is not an overstatement to say that while global convergence guarantees of ADMM under convex objective losses cement its utility, non-convex objectives offer superior reconstruction quality at the expense of these guarantees.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views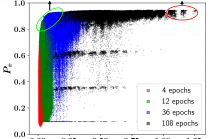
- Read more about EC-NAS: Energy Consumption Aware Tabular Benchmarks for Neural Architecture Search
- Log in to post comments
Energy consumption from the selection, training, and deployment of deep learning models has seen a significant uptick recently. This work aims to facilitate the design of energy-efficient deep learning models that require less computational resources and prioritize environmental sustainability by focusing on the energy consumption. Neural architecture search (NAS) benefits from tabular benchmarks, which evaluate NAS strategies cost-effectively through precomputed performance statistics. We advocate for including energy efficiency as an additional performance criterion in NAS.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views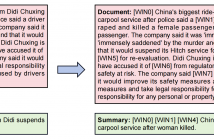
- Read more about Alleviating Hallucinations via Supportive Window Indexing in Abstractive Summarization
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Abstractive summarization models learned with maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) have been proven to produce hallucinatory content, which heavily limits their real-world
applicability. Preceding studies attribute this problem to the semantic insensitivity of MLE, and they compensate for it with additional unsupervised learning objectives that maximize the metrics of document-summary inferring, however, resulting in unstable and expensive model training. In this paper, we propose a novel supportive windows indexing
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Iterative Autoregressive Generation for Abstractive Summarization
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Abstractive summarization suffers from exposure bias caused by the teacher-forced maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) learning, that an autoregressive language model predicts the next token distribution conditioned on the exact pre-context during training while on its own predictions at inference. Preceding resolutions for this problem straightforwardly augment the pure token-level MLE with summary-level objectives.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views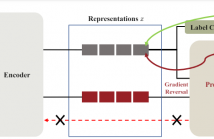
- Read more about Stethoscope-Guided Supervised Contrastive Learning for Cross-domain Adaptation on Respiratory Sound Classification
- Log in to post comments
Despite the remarkable advances in deep learning technology, achieving satisfactory performance in lung sound classification remains a challenge due to the scarcity of available data. Moreover, the respiratory sound samples are collected from a variety of electronic stethoscopes, which could potentially introduce biases into the trained models. When a significant distribution shift occurs within the test dataset or in a practical scenario, it can substantially decrease the performance.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views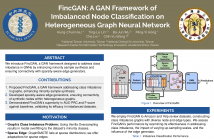
- Read more about FINCGAN: A GAN FRAMEWORK OF IMBALANCED NODE CLASSIFICATION ON HETEROGENEOUS GRAPH NEURAL NETWORK
- Log in to post comments
We introduce FincGAN, a GAN framework designed to address the class imbalance in GNNs by enhancing minority sample synthesis and ensuring connectivity with sparsity-aware edge generators.
- Categories:
 105 Views
105 Views
- Read more about MODEL-BASED LABEL-TO-IMAGE DIFFUSION FOR SEMI-SUPERVISED CHOROIDAL VESSEL SEGMENTATION
- Log in to post comments
Current successful choroidal vessel segmentation methods rely on large amounts of voxel-level annotations on the 3D optical coherence tomography images, which are hard and time-consuming. Semi-supervised learning solves this issue by enabling model learning from both unlabeled data and a limited amount of labeled data. A challenge is the defective pseudo labels generated for the unlabeled data. In this work, we propose a model-based label-to-image diffusion (MLD) framework for semi-supervised choroidal vessel segmentation.
ICASSP_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
Contrastive learning has demonstrated great effectiveness in representation learning especially for image classification tasks. However, there is still a shortage in the studies targeting regression tasks, and more specifically applications on hyperspectral data. In this paper, we propose a contrastive learning framework for the regression tasks for hyperspectral data. To this end, we provide a collection of transformations relevant for augmenting hyperspectral data, and investigate contrastive learning for regression.
ICASSP_PPT.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Unsupervised Acoustic Scene Mapping Based on Acoustic Features and Dimensionality Reduction
- Log in to post comments
Classical methods for acoustic scene mapping require the estimation of the time difference of arrival (TDOA) between microphones. Unfortunately, TDOA estimation is very sensitive to reverberation and additive noise. We introduce an unsupervised data-driven approach that exploits the natural structure of the data. Toward this goal, we adapt the recently proposed local conformal autoencoder (LOCA) – an offline deep learning scheme for extracting standardized data coordinates from measurements.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Poster for the paper "Revisiting Deep Generalized Canonical Correlation Analysis"
- Log in to post comments
Canonical correlation analysis (CCA) is a classic statistical method for discovering latent co-variation that underpins two or more observed random vectors. Several extensions and variations of CCA have been proposed that have strengthened our capabilities in terms of revealing common random factors from multiview datasets. In this work, we first revisit the most recent deterministic extensions of deep CCA and highlight the strengths and limitations of these state-of-the-art methods. Some methods allow trivial solutions, while others can miss weak common factors.
- Categories:
 49 Views
49 Views