
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about BOOSTING ZERO-SHOT HUMAN-OBJECT INTERACTION DETECTION WITH VISION-LANGUAGE TRANSFER
- Log in to post comments
Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection is a crucial task that involves localizing interactive human-object pairs and identifying the actions being performed. Most existing HOI detectors are supervised in nature and lack the ability of zero-shot discovery of unseen interactions. Recently, transformer-based methods have superseded the traditional CNN detectors by aggregating image-wide context but still suffer from the long-tail distribution problem in HOI. In this work, our primary focus is improving HOI detection in images, particularly in zero-shot scenarios.
- Categories:
 54 Views
54 Views
- Read more about Flow Dynamics Correction for Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Various research studies indicate that action recognition performance highly depends on the types of motions being extracted and how accurate the human actions are represented. In this paper, we investigate different optical flow, and features extracted from these optical flow that capturing both short-term and long-term motion dynamics. We perform power normalization on the magnitude component of optical flow for flow dynamics correction to boost subtle or dampen sudden motions.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about SEMANTIC DISTILLATION AND STRUCTURAL ALIGNMENT NETWORK FOR FAKE NEWS DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, the rapid proliferation of multi-modal fake news has posed potential harm across various sectors of society, making the detection of multi-modal fake news crucial. Most existing methods can not effectively reduce the redundant information and preserve both semantic and structural information. To address these problems, this paper proposes a semantic distillation and structural alignment (SDSA) network. We design an semantic distillation module for modality-specific features to preserve task-relevant semantic information and eliminate redundant information.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views
- Read more about TNFORMER: SINGLE-PASS MULTILINGUAL TEXT NORMALIZATION WITH A TRANSFORMER DECODER MODEL
- Log in to post comments
Text Normalization (TN) is a pivotal pre-processing procedure in speech synthesis systems, which converts diverse forms of text into a canonical form suitable for correct synthesis. This work introduces a novel model, TNFormer, which innovatively transforms the TN task into a next token prediction problem, leveraging the structure of GPT with only Transformer decoders for efficient, single-pass TN. The strength of TNFormer lies not only in its ability to identify Non-Standard Words that require normalization but also in its aptitude for context-driven normalization in a single pass.
- Categories:
 90 Views
90 Views
- Read more about TokenMotion: Motion-Guided Vision Transformer For Video Camouflaged Object Detection Via Learnable Token Selection
- Log in to post comments
The area of Video Camouflaged Object Detection (VCOD) presents unique challenges in the field of computer vision due to texture similarities between target objects and their surroundings, as well as irregular motion patterns caused by both objects and camera movement. In this paper, we introduce TokenMotion (TMNet), which employs a transformer-based model to enhance VCOD by extracting motion-guided features using a learnable token selection. Evaluated on the challenging MoCA-Mask dataset, TMNet achieves state-of-the-art performance in VCOD.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views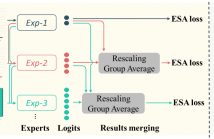
- Read more about ESA: Expert-and-Samples-Aware Incremental Learning under Longtail Distribution
- Log in to post comments
Most works in class incremental learning (CIL) assume disjoint sets of classes as tasks. Although a few works deal with overlapped sets of classes, they either assume a balanced data distribution or assume a mild imbalanced distribution. Instead, in this paper, we explore one of the understudied real-world CIL settings where (1) different tasks can share some classes but with new data samples, and (2) the training data of each task follows a long-tail distribution. We call this setting CIL-LT.
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views
- Read more about Multi-Source Dynamic Interactive Network Collaborative Reasoning Image Captioning
- Log in to post comments
Rich image and text features can largely improve the training of image captioning tasks. However, rich image and text features mean the incorporation of a large amount of unnecessary information. In our work, in order to fully explore and utilize the key information in images and text, we view the combination of image and text features as a data screening problem. The combination of image and text features is dynamically screened through a series of inference strategies with the aim of selecting the optimal image and text features.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Subspace-Based Co-Array Processing for Nested Arrays Without Eigendecomposition
- Log in to post comments
For the purpose of computational efficiency, we propose two subspace-based methods, but without eigendecomposition, to address the two typical problems in nested array processing, i.e., direction-of-arrival (DOA) estimation and noise elimination. In detail, to estimate DOA parameters, we judiciously arrange the segments extracted from the co-array model and then introduce a novel co-array-based orthogonal propagator method (COPM).
document.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about UNCERTAINTY-GUIDED PERSON SEARCH MODEL WITH AUXILIARY SHALLOW FEATURE EXPLORATION
- Log in to post comments
Person search is a unified system aimed at jointly localizing and identifying a person of interest from a gallery of whole scene images. Due to the inherent properties of the person search, it faces significant challenges of large-scale variations, inaccurate detection boxes, and crowded scenes. To address these issues, we proposed an uncertainty-guided framework coupled with auxiliary shallow feature exploration, which includes a shallow feature fusion module and an uncertaintyguided module.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about DATA DRIVEN GRAPHEME-TO-PHONEME REPRESENTATIONS FOR A LEXICON-FREE TEXT-TO-SPEECH
- Log in to post comments
Grapheme-to-Phoneme (G2P) is an essential first step in any modern, high-quality Text-to-Speech (TTS) system. Most of the current G2P systems rely on carefully hand-crafted lexicons developed by experts. This poses a two-fold problem. Firstly, the lexicons are generated using a fixed phoneme set, usually, ARPABET or IPA, which might not be the most optimal way to represent phonemes for all languages. Secondly, the man-hours required to produce such an expert lexicon are very high.
- Categories:
 75 Views
75 Views