
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about WIDROW-HOFF LMS ADALINE DEMONSTRATOR FOR SCHOOLS AND COLLEGES
- Log in to post comments
The Widrow-Hoff LMS (or ‘Adaline’) algorithm developed originally in 1960 is fundamental to the operation of countless signal processing machine learning systems in use even today. Bernard Widrow and Ted Hoff famously developed an Adaline machine demonstrator using basic analog off the shelf components to show how a ‘perceptron’ could be trained manually. This paper details the design and development of a fully digital Adaline Least-Mean-Square algorithm demonstrator.
- Categories:
 95 Views
95 Views
- Read more about SpatialCodec: Neural Spatial Speech Coding
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we address the challenge of encoding speech captured by a microphone array using deep learning techniques with the aim of preserving and accurately reconstructing crucial spatial cues embedded in multi-channel recordings. We propose a neural spatial audio coding framework that achieves a high compression ratio, leveraging single-channel neural sub-band codec and SpatialCodec.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views
- Read more about AdaPlus: Integrating Momentum and Precise Stepsize Adjustment on AdamW Basis
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes an efficient optimizer called AdaPlus which integrates Nesterov momentum and precise stepsize adjustment on AdamW basis. AdaPlus combines the advantages of AdamW, Nadam, and AdaBelief and, in particular, does not introduce any extra hyper-parameters. We perform extensive experimental evaluations on three machine learning tasks to validate the effectiveness of AdaPlus.
ICASSP.pdf
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about Exploring Meta Information for Audio-based Zero-Shot Bird Classification
- Log in to post comments
Advances in passive acoustic monitoring and machine learning have led to the procurement of vast datasets for computational bioacoustic research. Nevertheless, data scarcity is still an issue for rare and underrepresented species. This
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views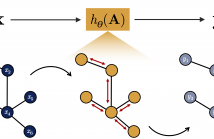
- Read more about Bayesian topology inference on partially known networks from input-output pairs
- Log in to post comments
We propose a sampling algorithm to perform system identification from a set of input-output graph signal pairs. The dynamics of the systems we study are given by a partially known adjacency matrix and a generic parametric graph filter of unknown parameters. The methodology we employ is built upon the principles of annealed Langevin diffusion. This enables us to draw samples from the posterior distribution instead of following the classical approach of point estimation using maximum likelihood.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views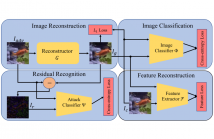
- Read more about Identifying Attack-Specific Signatures in Adversarial Examples
- Log in to post comments
The adversarial attack literature contains numerous algorithms for crafting perturbations which manipulate neural network predictions. Many of these adversarial attacks optimize inputs with the same constraints and have similar downstream impact on the models they attack. In this work, we first show how to reconstruct an adversarial perturbation, namely the difference between an adversarial example and the original natural image, from an adversarial example. Then, we classify reconstructed adversarial perturbations based on the algorithm that generated them.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views- Read more about Hardware Impairments-Aware Design of Noncoherent Grassmannian Constellations
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a robust algorithm for designing unstructured Grassmannian constellations for noncoherent MIMO communications that accounts for the effect of hardware impairments (HWIs) such as I/Q imbalance (IQI) and carrier frequency offset (CFO). The algorithm uses the minimum diversity product as a cost function to ensure full-diversity constellations. The constellation points in the Grassmannian are optimized to be robust against any value of the HWIs belonging to a given uncertainty set, the values of which are determined by the characteristics of the hardware used.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views- Read more about A Robust Quantile Huber Loss with Interpretable Parameter Adjustment in Distributional Reinforcement Learning
- Log in to post comments
Distributional Reinforcement Learning (RL) estimates return distribution mainly by learning quantile values via minimizing the quantile Huber loss function, entailing a threshold parameter often selected heuristically or via hyperparameter search, which may not generalize well and can be suboptimal. This paper introduces a generalized quantile Huber loss function derived from Wasserstein distance (WD) calculation between Gaussian distributions, capturing noise in predicted (current) and target (Bellmanupdated) quantile values.
- Categories:
 37 Views
37 Views
- Read more about RD-COST REGRESSION SPEED UP TECHNIQUE FOR VVC INTRA BLOCK PARTITIONING
- Log in to post comments
The last standard Versatile Video Codec (VVC) aims to improve the compression efficiency by saving around 50% of bitrate at the same quality compared to its predecessor High Efficiency Video Codec (HEVC). However, this comes with higher encoding complexity mainly due to a much larger number of block splits to be tested on the encoder side.
- Categories:
 57 Views
57 Views
- Read more about EXPLORATION OF VISUAL PROMPT IN GROUNDED PRE-TRAINED OPEN-SET DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Text prompts are crucial for generalizing pre-trained open-set object detection models to new categories. However, current methods for text prompts are limited as they require manual feedback when generalizing to new categories, which restricts their ability to model complex scenes, often leading to incorrect detection results. To address this limitation, we propose a novel visual prompt method that learns new category knowledge from a few labeled images, which generalizes the pre-trained detection model to the new category.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views