
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about GLMB 3D SPEAKER TRACKING WITH VIDEO-ASSISTED MULTI-CHANNEL AUDIO OPTIMIZATION FUNCTIONS
- Log in to post comments
Speaker tracking plays a significant role in numerous real-world human robot interaction (HRI) applications. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in utilizing multi-sensory information, such as complementary audio and visual signals, to address the challenges of speaker tracking. Despite the promising results, existing approaches still encounter difficulties in accurately determining the speaker’s true location, particularly in adverse conditions such as
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views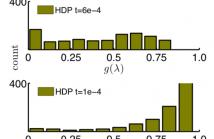
- Read more about High-order Tensor Pooling with Attention for Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We aim at capturing high-order statistics of feature vectors formed by a neural network, and propose end-to-end second- and higher-order pooling to form a tensor descriptor. Tensor descriptors require a robust similarity measure due to low numbers of aggregated vectors and the burstiness phenomenon, when a given feature appears more/less frequently than statistically expected. The Heat Diffusion Process (HDP) on a graph Laplacian is closely related to the Eigenvalue Power Normalization (EPN) of the covariance/auto-correlation matrix, whose inverse forms a loopy graph Laplacian.
- Categories:
 46 Views
46 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED REMOTE SENSING HAZE REMOVAL BASED ON SALIENCY-GUIDED TRANSMISSION REFINEMENT
- Log in to post comments
Haze causes information loss and quality degradation in remote sensing images. Unsupervised learning-based dehazing methods aim to reduce reliance on paired hazy images and their labels. However, complex mapping relationships often increase the difficulty in network convergence, resulting in color distortion and loss of texture details in remote sensing images. To address these issues, we propose an unsupervised haze removal method based on saliency-guided transmission refinement for remote sensing images.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about MTA: A Lightweight Multilingual Text Alignment Model for Cross-language Visual Word Sense Disambiguation
- Log in to post comments
Visual Word Sense Disambiguation (Visual-WSD), as a subtask of fine-grained image-text retrieval, requires a high level of language-vision understanding to capture and exploit the nuanced relationships between text and visual features. However, the cross-linguistic background only with limited contextual information is considered the most significant challenges for this task.
- Categories:
 28 Views
28 Views
- Read more about Improving Visual Quality and Transferability of Adversarial Attacks on Face Recognition Simultaneously with Adversarial Restoration
- Log in to post comments
Adversarial face examples possess two critical properties: Visual Quality and Transferability. However, existing approaches rarely address these properties simultaneously, leading to subpar results. To address this issue, we propose a novel adversarial attack technique known as Adversarial Restoration (AdvRestore), which enhances both visual quality and transferability of adversarial face examples by leveraging a face restoration prior. In our approach, we initially train a Restoration Latent Diffusion Model (RLDM) designed for face restoration.
slide.pptx
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Learned Video Compression with Spatial-Temporal Optimization
- Log in to post comments
Previous optical flow based video compression is gradually replaced by unsupervised deformable convolution (DCN) based method. This is mainly due to the fact that the motion vector (MV) estimated by the existing optical flow network
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about A Property-Guided Diffusion Model for Generating Molecular Graphs
- Log in to post comments
Inverse molecular generation is an essential task for drug discovery, and generative models offer a very promising avenue, especially when diffusion models are used. Despite their great success, existing methods are inherently limited by the lack of a semantic latent space that can not be navigated and perform targeted exploration to generate molecules with desired properties.
竖版-mcs.pdf
icassp.pptx
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about FreeTalker: Controllable Speech and Text-Driven Gesture Generation Based on Diffusion Models for Enhanced Speaker Naturalness
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Current talking avatars mostly generate co-speech gestures based on audio and text of the utterance, without considering the non-speaking motion of the speaker. Furthermore, previous works on co-speech gesture generation have designed network structures based on individual gesture datasets, which results in limited data volume, compromised generalizability, and restricted speaker movements.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about UNSUPERVISED LEARNING OF NEURAL SEMANTIC MAPPINGS WITH THE HUNGARIAN ALGORITHM FOR COMPOSITIONAL SEMANTICS
- Log in to post comments
Neural semantic parsing maps natural languages (NL) to equivalent formal semantics which are compositional and deduce the sentence meanings by composing smaller parts. To learn a well-defined semantics, semantic parsers must recognize small parts, which are semantic mappings between NL and semantic tokens. Attentions in recent neural models are usually explained as one-on-one semantic mappings. However, attention weights with end-to-end training are shown only weakly correlated with human-labeled mappings. Despite the usefulness, supervised mappings are expensive.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about 1-D Spatial Attention in Binarized Convolutional Neural Networks
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a structure called SPBNet for enhancing binarized convolutional neural networks (BCNNs) using a low-cost 1-D spatial attention structure. Attention blocks can compensate for the performance drop in BCNNs. However, the hardware overhead of complex attention blocks can be a significant burden in BCNNs. The proposed attention block consists of low-cost 1-D height-wise and width-wise 1-D convolutions, It has the attention bias to adjust the effects of attended features in ×0.5 − ×1.5.
- Categories:
 155 Views
155 Views