
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
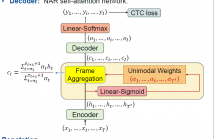
This paper works on non-autoregressive automatic speech recognition. A unimodal aggregation (UMA) is proposed to segment and integrate the feature frames that belong to the same text token, and thus to learn better feature representations for text tokens. The frame-wise features and weights are both derived from an encoder. Then, the feature frames with unimodal weights are integrated and further processed by a decoder. Connectionist temporal classification (CTC) loss is applied for training.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about META REPRESENTATION LEARNING METHOD FOR ROBUST SPEAKER VERIFICATION IN UNSEEN DOMAINS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a meta representation learning method for robust speaker verification (SV) in unseen domains. It is known that the existing embedding learning based SV systems may suffer from domain mismatch issues. To address this, we propose an episodic training procedure to compensate domain mismatch conditions at runtime. Specifically, episodes are constructed with domain balanced episodic sampling from two different domains, and a new domain alignment (DA) module is added besides the feature extractor (FE) and classifier to existing network structures.
- Categories:
 58 Views
58 Views
- Read more about UNRAVELING EXPLAINABLE REINFORCEMENT LEARNING USING BEHAVIOR TREE STRUCTURES
- Log in to post comments
The black-box characteristic of deep reinforcement learning restricts the safe and scalable application of decision models in practical deployment. Existing interpretability methods for deep reinforcement learning models are often inadequate in providing comprehensive insights and generating logical sequential decisions.
In this study, we propose an innovative framework called XRLBT, which introduces the behavior tree structure to explainable reinforcement learning.
poster (1).pdf
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views- Read more about Gravitated Latent Space Loss Generated by Metric Tensor for High-Dynamic Range Imaging
- Log in to post comments
High Dynamic Range (HDR) imaging seeks to enhance image quality by combining multiple Low Dynamic Range (LDR) images captured at varying exposure levels. Traditional deep learning approaches often employ reconstruction loss, but this method can lead to ambiguities in feature space during training. To address this issue, we present a new loss function, termed Gravitated Latent Space (GLS) loss, that leverages a metric tensor to introduce a form of virtual gravity within the latent space. This feature helps the model in overcoming saddle points more effectively.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about FAST PERSONALIZED TEXT TO IMAGE SYNTHESIS WITH ATTENTION INJECTION
- Log in to post comments
Currently, personalized image generation methods mostly require considerable time to finetune and often overfit the concept resulting in generated images that are similar to custom concepts but difficult to edit by prompts. We propose an effective and fast approach that could balance the text-image consistency and identity consistency of the generated image and reference image. Our method can generate personalized images without any fine-tuning while maintaining the inherent text-to-image generation ability of diffusion models.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views
- Read more about Physics-Guided Deep Scatter Estimation by Weakly Supervision for Quantitative SPECT
- Log in to post comments
Accurate scatter estimation is important in quantitative SPECT for improving image contrast and accuracy. With a large number of photon histories, Monte-Carlo (MC) simulation can yield accurate scatter estimation, but is computationally expensive. Recent deep learning-based approaches can yield accurate scatter estimates quickly, yet full MC simulation is still required to generate scatter estimates as ground truth labels for all training data.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views
- Read more about DOMAIN-WISE INVARIANT LEARNING FOR PANOPTIC SCENE GRAPH GENERATION
- Log in to post comments
Panoptic Scene Graph Generation (PSG) involves the detection of objects and the prediction of their corresponding relationships (predicates). However, the presence of biased predicate annotations poses a significant challenge for PSG models, as it hinders their ability to establish a clear decision boundary among different predicates. This issue substantially impedes the practical utility and real-world applicability of PSG models.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about A Novel Iterative Thresholding Algorithm for Arctangent Regularization Problem
- Log in to post comments
In this work, we derive the proximity operator of an arctangent penalty, which is expressed using hyperbolic functions of sine and cosine. This penalty is then applied to sparse signal recovery, and an efficient arctangent regularization iterative thresholding (ARIT) algorithm is proposed, offering closed-form solutions for the subproblems associated with the arctangent penalty.
poster_ARIT.pdf
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Video-Language Graph Convolutional Network for Human Action Recognition
- Log in to post comments
Transferring visual language models (VLMs) from the image domain to the video domain has recently yielded great success on human action recognition tasks. However, standard recognition paradigms overlook fine-grained action parsing knowledge that could enhance the recognition accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel method that leverages both coarse-grained and fine-grained knowledge to recognize human actions in videos. Our method consists of a video-language graph convolutional network that integrates and fuses multi-modal knowledge in a progressive manner.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about Highlight removal network based on an improved dichromatic reflection model
- Log in to post comments
State-of-the-art highlight removal methods still face the problems of color inconsistencies between highlight region and background, and content unreality in highlight areas.
To solve these two problems, we propose a novel adaptive highlight-aware network for specular highlight removal based on an improved dichromatic reflection model.
For color inconsistencies, we propose an adaptive highlight-aware (AHA) module to perceive the complete highlight information including the location and the scale of the specular highlight.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views