- Transducers
- Spatial and Multichannel Audio
- Source Separation and Signal Enhancement
- Room Acoustics and Acoustic System Modeling
- Network Audio
- Audio for Multimedia
- Audio Processing Systems
- Audio Coding
- Audio Analysis and Synthesis
- Active Noise Control
- Auditory Modeling and Hearing Aids
- Bioacoustics and Medical Acoustics
- Music Signal Processing
- Loudspeaker and Microphone Array Signal Processing
- Echo Cancellation
- Content-Based Audio Processing

- Read more about Hierarchy-aware Loss Function on a Tree Structured Label Space for Audio Event Detection
- Log in to post comments
The paper introduces a hierarchy-aware loss function in a Deep Neural Network for an audio event detection task that has a bi-level tree structured label space. The goal is not only to improve audio event detection performance at all levels in the label hierarchy, but also to produce better audio embeddings. We exploit the label tree structure to preserve that information in the hierarchy-aware loss function. Two different loss functions are separately employed. First, a triplet loss with probabilistic multi-level batch mining is introduced.
- Categories:
 62 Views
62 Views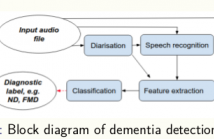
- Read more about COMPUTATIONAL COGNITIVE ASSESSMENT: INVESTIGATING THE USE OF AN INTELLIGENT VIRTUAL AGENT FOR THE DETECTION OF EARLY SIGNS OF DEMENTIA
- Log in to post comments
The ageing population has caused a marked increased in the number of people with cognitive decline linked with dementia. Thus, current diagnostic services are overstretched, and there is an urgent need for automating parts of the assessment process. In previous work, we demonstrated how a stratification tool built around an Intelligent Virtual Agent (IVA) eliciting a conversation by asking memory-probing questions, was able to accurately distinguish between people with a neuro-degenerative disorder (ND) and a functional memory disorder (FMD).
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about Overlap-Add Windows with Maximum Energy Concentration for Speech and Audio Processing
- Log in to post comments
Processing of speech and audio signals with time-frequency representations require windowing methods which allow perfect reconstruction of the original signal and where processing artifacts have a predictable behavior. The most common approach for this purpose is overlap-add windowing, where signal segments are windowed before and after processing. Commonly used windows include the half-sine and a Kaiser-Bessel derived window. The latter is an approximation of the discrete prolate spherical sequence, and thus a maximum energy concentration window, adapted for overlap-add.
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about FINE-TUNING APPROACH TO NIR FACE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Despite extensive researches for face recognition (FR), it is still difficult to apply deep CNN models to NIR FR due to a lack of training data. In this study, we propose a fine-tuning approach to allow deep CNN models to be applied to NIR FR with small training datasets. In the proposed approach, parameters of deep CNN models for RGB FR are utilized as initial parameters to train deep CNN models for NIR FR. The proposed approach has two main advantages: 1) High NIR FR performances can be achieved with very small public training datasets.
- Categories:
 44 Views
44 Views
- Read more about DIFFERENTIALLY PRIVATE GREEDY DECISION FOREST
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about COMPACT CONVOLUTIONAL RECURRENT NEURAL NETWORKS VIA BINARIZATION FOR SPEECH EMOTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Despite the great advances, most of the recently developed automatic speech recognition systems focus on working in a server-client manner, and thus often require a high computational cost, such as the storage size and memory accesses. This, however, does not satisfy the increasing demand for a succinct model that can run smoothly in embedded devices like smartphones.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about DISTRIBUTED TRACKING OF MANEUVERING TARGET: A FINITE-TIME ALGORITHM
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Inter- and Intra- Patient ECG Heartbeat Classification For Arrhythmia Detection: a Sequence to Sequence Deep Learning Approach
- Log in to post comments
Electrocardiogram (ECG) signal is a common and powerful tool to study heart function and diagnose several abnormal arrhythmias. While there have been remarkable improvements in cardiac arrhythmia classification methods, they still cannot offer acceptable performance in detecting different heart conditions, especially when dealing with imbalanced datasets. In this paper, we propose a solution to address this limitation of current classification approaches by developing an automatic heartbeat classification method using deep convolutional neural networks and sequence to sequence models.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about Bluetooth based Indoor Localization using Triplet Embeddings
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views