
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about END-TO-END LANGUAGE RECOGNITION USING ATTENTION BASED HIERARCHICAL GATED RECURRENT UNIT MODELS
- Log in to post comments
The task of automatic language identification (LID) involving multiple dialects of the same language family on short speech recordings is a challenging problem. This can be further complicated for short-duration audio snippets in the presence of noise sources. In these scenarios, the identity of the language/dialect may be reliably present only in parts of the speech embedded in the temporal sequence.
- Categories:
 40 Views
40 Views- Read more about Adaptive Subspace Detector in High Dimensional Space with Insufficient Training Data
- Log in to post comments
Adaptive subspace detectors (ASD) generalize matched subspace detectors (MSD) by accounting for possible correlation. Both ASD and MSD are derived using the generalized likelihood ratio test (GLRT). While MSD assumes there is no correlation between observations, ASD estimates a sample covariance matrix of possibly correlated samples using signal-free observations. In this paper, we address the performance of the ASD when the number of secondary data is insufficient and the observed signal lies in higher dimensional space.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views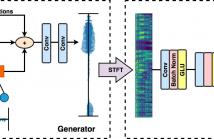
- Read more about Perceptually-motivated environment-specific speech enhancement
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces a deep learning approach to enhance speech recordings made in a specific environment. A single neural network learns to ameliorate several types of recording artifacts, including noise, reverberation, and non-linear equalization. The method relies on a new perceptual loss function that combines adversarial loss with spectrogram features. Both subjective and objective evaluations show that the proposed approach improves on state-of-the-art baseline methods.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about DEEP EMBEDDINGS FOR RARE AUDIO EVENT DETECTION WITH IMBALANCED DATA
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a method to handle data imbalance for classification with neural networks, and apply it to acoustic event detection (AED) problem. The common approach to tackle data imbalance is to use class-weights in the objective function while training. An existing more sophisticated approach is to map the input to clusters in an embedding space, so that learning is locally balanced by incorporating inter-cluster and inter-class margins. On these lines, we propose a method to learn the embedding using a novel objective function, called triple-header cross entropy.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about TV-DCT: Method to Impute Gene Expression Data Using DCT Based Sparsity and Total Variation Denoising
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about SEQUENTIAL STRUCTURED DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR BLOCK SPARSE REPRESENTATIONS
- Log in to post comments
Dictionary learning algorithms have been successfully applied to a number of signal and image processing problems. In some applications however, the observed signals may have a multi-subpsace structure that enables block-sparse signal representations. Based on the observation that the observed signals can be approximated as a sum of low rank matrices, a new algorithm for learning a block-structured dictionary for block-sparse signal representations is proposed.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Motion Artefact Removal in Functional Near-InfraRed Spectroscopy Signals based on Robust Estimation
- Log in to post comments
Functional Near-InfraRed Spectroscopy (fNIRS) has gained widespread acceptance as a non-invasive neuroimaging modality for monitoring functional brain activities. fNIRS uses light in the near infra-red spectrum (600-900 nm) to penetrate human brain tissues and estimates the oxygenation conditions based on the proportion of light absorbed. In order to get reliable results, artefacts and noise need to be separated from fNIRS physiological signals. This paper focuses on removing motion-related artefacts. A new motion artefact removal algorithm based on robust parameter estimation is proposed.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about STOCHASTIC DATA-DRIVEN HARDWARE RESILIENCE TO EFFICIENTLY TRAIN INFERENCE MODELS FOR STOCHASTIC HARDWARE IMPLEMENTATIONS
- Log in to post comments
Machine-learning algorithms are being employed in an increasing range of applications, spanning high-performance and energy-constrained platforms. It has been noted that the statistical nature of the algorithms can open up new opportunities for throughput and energy efficiency, by moving hardware into design regimes not limited to deterministic models of computation. This work aims to enable high accuracy in machine-learning inference systems, where computations are substantially affected by hardware variability.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Sell-corpus: an Open Source Multiple Accented Chinese-english Speech Corpus for L2 English Learning Assessment
- Log in to post comments
We present SELL-CORPUS, a multiple accented speech corpus for L2 English learning in China, aiming at the potential research of multiple accented acoustic model, mispronunciation detection and pronunciation assessment for future nationwide oral English tests. Our corpus contains 31.6 hour speech recordings contributed by 389 volunteer speakers, including 186 males and 203 females. Our corpus covers seven major regional dialects and provides a baseline for Chinese multiple accented automatic speech recognition system. We released our speech corpus to the public for academic research.
 95 Views
95 Views
- Read more about DETECTING GAS VAPOR LEAKS THROUGH UNCALIBRATED SENSOR BASED CPS
- Log in to post comments
CPS comprised of ordinary people or first responders is proposed to detect gas vapor in open air.
This CPS will use low-cost sensors coupled to smart phones or mobile devices.
The efficacy of CPS hinges on its ability to address technical challenges stemming from the fact that sensors may produce different results under the same conditions due to sensor drift, noise, and/or resolution errors.
The proposed system makes use of time-varying signals produced by sensors to detect gas leaks. Sensors sample the gas vapor level in a continuous manner
icassp2019.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views