
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Robust Room Equalization Using Sparse Sound-Field Reconstruction
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
In this research, we aim to propose a data preprocessing framework particularly for financial sector to generate the rating data as input to the collaborative system. First, clustering technique is applied to cluster all users based on their demographic information which might be able to differentiate the customers’ background. Then, for each customer group, the importance of demographic characteristics which are highly associated with financial products purchasing are analyzed by the proposed fuzzy integral technique.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Evaluating Salience Representations for Cross-Modal Retrieval of Western Classical Music Recordings
- Log in to post comments
In this contribution, we consider a cross-modal retrieval scenario of Western classical music. Given a short monophonic musical theme in symbolic notation as query, the objective is to find relevant audio recordings in a database. A major challenge of this retrieval task is the possible difference in the degree of polyphony between the monophonic query and the music recordings. Previous studies for popular music addressed this issue by performing the cross-modal comparison based on predominant melodies extracted from the recordings.
- Categories:
 74 Views
74 Views
- Read more about View-Invariant Action Recognition From RGB Data via 3D Pose Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a novel view-invariant action recognition method using a single monocular RGB camera. View-invariance remains a very challenging topic in 2D action recognition due to the lack of 3D information in RGB images. Most successful approaches make use of the concept of knowledge transfer by projecting 3D synthetic data to multiple viewpoints. Instead of relying on knowledge transfer, we propose to augment the RGB data by a third dimension by means of 3D skeleton estimation from 2D images using a CNN-based pose estimator.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views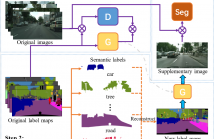
- Read more about Poster of pixel level data augmentation for semantic image segmentation using generative adversarial networks
- Log in to post comments
Semantic segmentation is one of the basic topics in computer vision, it aims to assign semantic labels to every pixel of an image. Unbalanced semantic label distribution could have a negative influence on segmentation accuracy. In this paper, we investigate using data augmentation approach to balance the label distribution in order to improve segmentation performance. We propose using generative adversarial networks (GANs) to generate realistic images for improving the performance of semantic segmentation networks.
- Categories:
 131 Views
131 Views

- Read more about Robust gridless sound field decomposition based on structured eciprocity gap functional in spherical harmonic domain
- Log in to post comments
A sound field reconstruction method for a region including sources is proposed. Under the assumption of spatial sparsity of the sources,this reconstruction problem has been solved by using sparse decomposition algorithms with the discretization of the target region. Since this discretization leads to the off-grid problem, we previously proposed a gridless sound field decomposition method based on the reciprocity gap functional in the spherical harmonic domain.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Global and Local Mode-domain Adaptive Algorithms for Spatial Active Noise Control Using Higher-order Sources
- Log in to post comments
The aim of spatial active noise control (ANC) is to attenuate noise over a certain space. Although a large-scale system is required to
achieve spatial ANC, mode-domain signal processing makes it possible to reduce the computational cost and improve the performance.
A higher-order source (HOS) has an advantage in sound field control due to its controllable directivity patterns. An array of HOS
can suppress an undesired exterior sound propagation while occupying a smaller physical space than a conventional omnidirectional
- Categories:
 60 Views
60 Views
- Read more about Fast Implementation of Double-coupled Nonnegative Canonical Polyadic Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Real-world data exhibiting high order/dimensionality and various couplings are linked to each other since they share
some common characteristics. Coupled tensor decomposition has become a popular technique for group analysis in recent
years, especially for simultaneous analysis of multi-block tensor data with common information. To address the multi-
block tensor data, we propose a fast double-coupled nonnegative Canonical Polyadic Decomposition (FDC-NCPD)
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Models of visually grounded speech signal pay attention to nouns: a bilingual experiment on English and Japanese
- Log in to post comments
We investigate the behaviour of attention in neural models of visually grounded speech trained on two languages: English and Japanese. Experimental results show that attention focuses on nouns and this behaviour holds true for two very typologically different languages. We also draw parallels between artificial neural attention and human attention and show that neural attention focuses on word endings as it has been theorised for human attention. Finally, we investigate how two visually grounded monolingual models can be used to perform cross-lingual speech-to-speech retrieval.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views