
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The 2019 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Enhanced Recurrent Neural Network for Combining Static and Dynamic Features for Credit Card Default Prediction
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning models have been shown to be capable of extracting high-level representations from the increasing amount of customer-level data generated via fast-growing financial activities. In financial data, dynamic features that evolve with time are commonly observed. However, such time dependencies are often ignored in classical classification models. In this study, we propose to learn a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) feature extractor with GRU on credit card payment history to leverage the time dependencies embedded in these dynamic features.
- Categories:
 135 Views
135 Views
- Read more about INCREMENTAL TRANSFER LEARNING IN TWO-PASS INFORMATION BOTTLENECK BASED SPEAKER DIARIZATION SYSTEM FOR MEETINGS
- Log in to post comments
The two-pass information bottleneck (TPIB) based speaker diarization system operates independently on different conversational recordings. TPIB system does not consider previously learned speaker discriminative information while diarizing new conversations. Hence, the real time factor (RTF) of TPIB system is high owing to the training time required for the artificial neural network (ANN).
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Using recurrences in time and frequency within U-net architecture for speech enhancement
- Log in to post comments
When designing fully-convolutional neural network, there is a trade-off between receptive field size, number of parameters and spatial resolution of features in deeper layers of the network. In this work we present a novel network design based on combination of many convolutional and recurrent layers that solves these dilemmas. We compare our solution with U-nets based models known from the literature and other baseline models on speech enhancement task.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views
- Read more about MULTI-SCALE SPATIAL-TEMPORAL NETWORK FOR PERSON RE-IDENTIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
last_version1.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Deep Learning Features for Robust Detection of Acoustic Events in Sleep-Disordered Breathing
- Log in to post comments
Sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) is a serious and prevalent condition, and acoustic analysis via consumer devices (e.g. smartphones) offers a low-cost solution to screening for it. We present a novel approach for the acoustic identification of SDB sounds, such as snoring, using bottleneck features learned from a corpus of whole-night sound recordings. Two types of bottleneck features are described, obtained by applying a deep autoencoder to the output of an auditory model or a short-term autocorrelation analysis.
icassp2019-poster.pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Langevin-based Strategy for Efficient Proposal Adaptation in Population Monte Carlo
- Log in to post comments
Population Monte Carlo (PMC) algorithms are a family of
adaptive importance sampling (AIS) methods for approximating
integrals in Bayesian inference. In this paper, we propose
a novel PMC algorithm that combines recent advances
in the AIS and the optimization literatures. In such a way, the
proposal densities are adapted according to the past weighted
samples via a local resampling that preserves the diversity,
but we also exploit the geometry of the targeted distribution.
A scaled Langevin strategy with Newton-based scaling metric
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about 3D VISUAL SPEECH ANIMATION USING 2D VIDEOS
- Log in to post comments
In visual speech animation, lip motion accuracy is of paramount importance for speech intelligibility, especially for the hard of hearing or foreign language learners. We present an approach for visual speech animation that uses tracked lip motion in front-view 2D videos of a real speaker to drive the lip motion of a synthetic 3D head. This makes use of a 3D morphable model (3DMM), built using 3D synthetic head poses, with corresponding landmarks identified in the 2D videos and the 3DMM.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views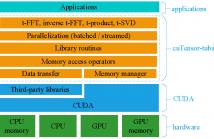
- Read more about CUTENSOR-TUBAL: OPTIMIZED GPU LIBRARY FOR LOW-TUBAL-RANK TENSORS
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we optimize the computations of third-order low-tubal-rank tensor operations on many-core GPUs. Tensor operations are compute-intensive and existing studies optimize such operations in a case-by-case manner, which can be inefficient and error-prone. We develop and optimize a BLAS-like library for the low-tubal-rank tensor model called cuTensor-tubal, which includes efficient GPU primitives for tensor operations and key processes. We compute tensor operations in the frequency domain and fully exploit tube-wise and slice-wise parallelisms.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
Obtaining aligned spectral pairs in case of non-parallel data for stand-alone Voice Conversion (VC) technique is a challenging research problem. Unsupervised alignment algorithm, namely, an Iterative combination of a Nearest Neighbor search step and a Conversion step Alignment (INCA) iteratively tries to align the spectral features by minimizing the Euclidean distance metric between the intermediate converted and the target spectral feature vectors.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views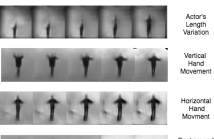
- Read more about LEARNING TEMPORAL INFORMATION FROM SPATIAL INFORMATION USING CAPSNETS FOR HUMAN ACTION RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
Capsule Networks (CapsNets) are recently introduced to overcome some of the shortcomings of traditional Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs). CapsNets replace neurons in CNNs with vectors to retain spatial relationships among the features. In this paper, we propose a CapsNet architecture that employs individual video frames for human action recognition without explicitly extracting motion information. We also propose weight pooling to reduce the computational complexity and improve the classification accuracy by appropriately removing some of the extracted features.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views