
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

Hypothesis-level combination between multiple models can often yield gains in speech recognition. However, all models in the ensemble are usually restricted to use the same audio segmentation times. This paper proposes to generalise hypothesis-level combination, allowing the use of different audio segmentation times between the models, by splitting and re-joining the hypothesised N-best lists in time. A hypothesis tree method is also proposed to distribute hypothesis posteriors among the constituent words, to facilitate such splitting when per-word scores are not available.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about SEMI-SUPERVISED SKIN LESION SEGMENTATION WITH LEARNING MODEL CONFIDENCE
- Log in to post comments
poster-xzq.pdf
- Categories:
 3 Views
3 Views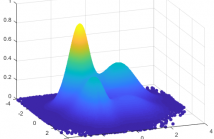
- Read more about Independent Vector Analysis using Semi-Parametric Density Estimation via Multivariate Entropy Maximization
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
Due to the wide use of multi-sensor technology, analysis of multiple sets of data is at the heart of many challenging engineering problems. Independent vector analysis (IVA), a recent generalization of independent component analysis (ICA), enables the joint analysis of datasets and extraction of latent sources through the use of a simple yet effective generative model. However, the success of IVA is tied to proper estimation of the probability density function (PDF) of the multivariate latent sources; information that is generally unknown.
- Categories:
 96 Views
96 Views
Prosody is an integral part of communication, but remains an open problem in state-of-the-art speech synthesis. There are two major issues faced when modelling prosody: (1) prosody varies at a slower rate compared with other content in the acoustic signal (e.g. segmental information and background noise); (2) determining appropriate prosody without sufficient context is an ill-posed problem. In this paper, we propose solutions to both these issues. To mitigate the challenge of modelling a slow-varying signal, we learn to disentangle prosodic information using a word level representation.
poster.pdf
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about SIG2SIG : SIGNAL TRANSLATION NETWORKS TO TAKE THE REMAINS OF THE PAST
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Radar Clutter Classification Using Expectation-Maximization Method
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Read more about Amplitude Matching: Majorization-Minimization Algorithm For Sound Field Control Only With Amplitude Constraint
- Log in to post comments
ICASSP2021.pdf
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
- Read more about DEEPF0: END-TO-END FUNDAMENTAL FREQUENCY ESTIMATION FOR MUSIC AND SPEECH SIGNALS
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel pitch estimation technique called DeepF0, which leverages the available annotated data to directly learns from the raw audio in a data-driven manner. F0 estimation is important in various speech processing and music information retrieval applications. Existing deep learning models for pitch estimations have relatively limited learning capabilities due to their shallow receptive field. The proposed model addresses this issue by extending the receptive field of a network by introducing the dilated convolutional blocks into the network.
- Categories:
 124 Views
124 Views
- Read more about Differential Convolution Feature Guided Deep Multi-Scale Multiple Instance Learning for Aerial Scene Classification
- Log in to post comments
Aerial image classification is challenging for current deep learning models due to the varied geo-spatial object scales and the complicated scene spatial arrangement. Thus, it is necessary to stress the key local feature response from a variety of scales so as to represent discriminative convolutional features. In this paper, we propose a deep multi-scale multiple instance learning (DMSMIL) framework to tackle the above challenges. Firstly, we develop a differential multi-scale dilated convolution feature extractor to exploit the different patterns from different scales.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views