
ICASSP 2022 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2022 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about MULTILINGUAL SECOND-PASS RESCORING FOR AUTOMATIC SPEECH RECOGNITION SYSTEMS
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views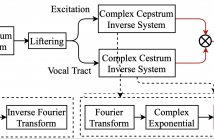
Most deep learning-based speech enhancement methods operate directly on time-frequency representations or learned features without making use of the model of speech production. This work proposes a new speech enhancement method based on neural homomorphic synthesis. The speech signal is firstly decomposed into excitation and vocal tract with complex cepstrum analysis. Then, two complex-valued neural networks are applied to estimate the target complex spectrum of the decomposed components. Finally, the time-domain speech signal is synthesized from the estimated excitation and vocal tract.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
Deep neural network (DNN) watermarking is one of the main techniques to protect the DNN. Although various DNN watermarking schemes have been proposed, none of them is able to resist the DNN encryption. In this paper, we propose an encryption resistent DNN watermarking scheme, which is able to resist the parameter shuffling based DNN encryption. Unlike the existing schemes which use the kernels separately for watermarking embedding, we propose to embed the watermark into the fused kernels to resist the parameter shuffling.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Quantum Federated Learning with Quantum Data
- Log in to post comments
Mahdi Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about END-TO-END ASR-ENHANCED NEURAL NETWORK FOR ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents an approach to Alzheimer’s disease (AD) diagnosis from spontaneous speech using an end-to-end ASR-enhanced neural network. Under the condition that only audio data are provided and accurate transcripts are unavailable, this paper proposes a system that can analyze utterances to differentiate between AD patients, healthy controls, and individuals with mild cognitive impairment. The ASR-enhanced model comprises automatic speech recognition (ASR) with an encoder-decoder structure and the encoder followed by an AD classification network.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about Modeling Beats And Downbeats With A Time-frequency Transformer
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about TO CATCH A CHORUS, VERSE, INTRO, OR ANYTHING ELSE: ANALYZING A SONG WITH STRUCTURAL FUNCTIONS
- Log in to post comments
Conventional music structure analysis algorithms aim to divide a song into segments and to group them with abstract labels (e.g., ‘A’, ‘B’, and ‘C’). However, explicitly identifying the function of each segment (e.g., ‘verse’ or ‘chorus’) is rarely attempted, but has many applications. We introduce a multi-task deep learning framework to model these structural semantic labels directly from audio by estimating "verseness," "chorusness," and so forth, as a function of time.
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about Adaptive Group Testing with Mismatched Models
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about The Mirrornet : Learning Audio Synthesizer Controls Inspired by Sensorimotor Interaction
- Log in to post comments
Experiments to understand the sensorimotor neural interactions in the human cortical speech system support the existence of a bidirectional flow of interactions between the auditory and motor regions. Their key function is to enable the brain to ‘learn’ how to control the vocal tract for speech production. This idea is the impetus for the recently proposed "MirrorNet", a constrained autoencoder architecture.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Aerial Base Station Placement Leveraging Radio Tomographic Maps
- Log in to post comments
Mobile base stations on board unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs)
promise to deliver connectivity to those areas where the
terrestrial infrastructure is overloaded, damaged, or absent. A
fundamental problem in this context involves determining a
minimal set of locations in 3D space where such aerial base
stations (ABSs) must be deployed to provide coverage to a set of
users. While nearly all existing approaches rely on average
characterizations of the propagation medium, this work
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views