
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Bandwidth Extension is All You Need
- Log in to post comments
Speech generation and enhancement have seen recent breakthroughs in quality thanks to deep learning. These methods typically operate at a limited sampling rate of 16-22kHz due to computational complexity and available datasets. This limitation imposes a gap between the output of such methods and that of high-fidelity (≥44kHz) real-world audio applications. This paper proposes a new bandwidth extension (BWE) method that expands 8-16kHz speech signals to 48kHz. The method is based on a feed-forward WaveNet architecture trained with a GAN-based deep feature loss.
- Categories:
 133 Views
133 Views
- Read more about CASS-NAT: CTC Alignment-Based Single Step Non-Autoregressive Transformer for Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
We propose a CTC alignment-based single step non-autoregressive transformer (CASS-NAT) for speech recognition. Specifically, the CTC alignment contains the information of (a) the number of tokens for decoder input, and (b) the time span of acoustics for each token. The information are used to extract acoustic representation for each token in parallel, referred to as token-level acoustic embedding which substitutes the word embedding in autoregressive transformer (AT) to achieve parallel generation in decoder.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about BI-APC: BIDIRECTIONAL AUTOREGRESSIVE PREDICTIVE CODING FOR UNSUPERVISED PRE-TRAINING AND ITS APPLICATION TO CHILDREN’S ASR
- Log in to post comments
We present a bidirectional unsupervised model pre-training (UPT) method and apply it to children’s automatic speech recognition (ASR). An obstacle to improving child ASR is the scarcity of child speech databases. A common approach to alleviate this problem is model pre-training using data from adult speech. Pre-training can be done using supervised (SPT) or unsupervised methods, depending on the availability of annotations. Typically, SPT performs better. In this paper, we focus on UPT to address the situations when pre-training data are unlabeled.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Mispronunciation Detection in Non-native (L2) English with Uncertainty Modeling
- Log in to post comments
A common approach to the automatic detection of mispronunciation in language learning is to recognize the phonemes produced by a student and compare it to the expected pronunciation of a native speaker. This approach makes two simplifying assumptions: a) phonemes can be recognized from speech with high accuracy, b) there is a single correct way for a sentence to be pronounced. These assumptions do not always hold, which can result in a significant amount of false mispronunciation alarms.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about Mispronunciation Detection in Non-native (L2) English with Uncertainty Modeling
- Log in to post comments
A common approach to the automatic detection of mispronunciation in language learning is to recognize the phonemes produced by a student and compare it to the expected pronunciation of a native speaker. This approach makes two simplifying assumptions: a) phonemes can be recognized from speech with high accuracy, b) there is a single correct way for a sentence to be pronounced. These assumptions do not always hold, which can result in a significant amount of false mispronunciation alarms.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views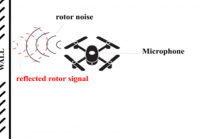
In this paper, we propose a method to estimate the proximity of an acoustic reflector, e.g., a wall, using ego-noise, i.e., the noise produced by the moving parts of a listening robot. This is achieved by estimating the times of arrival of acoustic echoes reflected from the surface. Simulated experiments show that the proposed non-intrusive approach is capable of accurately estimating the distance of a reflector up to 1 meter and outperforms a previously proposed intrusive approach under loud ego-noise conditions.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about KALMANNET: DATA-DRIVEN KALMAN FILTERING
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 51 Views
51 Views
- Read more about STRUCTURED SUPPORT EXPLORATION FOR MULTILAYER SPARSE MATRIX FACTORIZATION
- Log in to post comments
Matrix factorization with sparsity constraints plays an important role in many machine learning and signal processing problems such as dictionary learning, data visualization, dimension reduction. Among the most popular tools for sparse matrix factorization are proximal algorithms, a family of algorithms based on proximal operators. In this paper, we address two problems with the application of proximal algorithms to sparse matrix factorization. On the one hand, we analyze a weakness of proximal algorithms in sparse matrix factorization: the premature convergence of the support.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
Few-shot image classification aims to classify unseen classes with limited labelled samples. Recent works benefit from the meta-learning process with episodic tasks and can fast adapt to class from training to testing. Due to the limited number of samples for each task, the initial embedding network for meta-learning becomes an essential component and can largely affect the performance in practice. To this end, most of the existing methods highly rely on the efficient embedding network.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about A PARALLELIZABLE LATTICE RESCORING STRATEGY WITH NEURAL LANGUAGE MODELS
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a parallel computation strategy and a posterior-based lattice expansion algorithm for efficient lattice rescoring with neural language models (LMs) for automatic speech recognition. First, lattices from first-pass decoding are expanded by the proposed posterior-based lattice expansion algorithm. Second, each expanded lattice is converted into a minimal list of hypotheses that covers every arc. Each hypothesis is constrained to be the best path for at least one arc it includes.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views