
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about NON-PARALLEL MANY-TO-MANY VOICE CONVERSION BY KNOWLEDGE TRANSFER FROM A TEXT-TO-SPEECH MODEL
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about Context-Aware Prosody Correction for Text-Based Speech Editing
- Log in to post comments
Text-based speech editors expedite the process of editing speech recordings by permitting editing via intuitive cut, copy, and paste operations on a speech transcript. A major drawback of current systems, however, is that edited recordings often sound unnatural because of prosody mismatches around edited regions. In our work, we propose a new context-aware method for more natural sounding text-based editing of speech.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views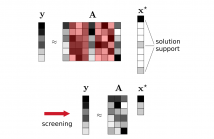
- Read more about SAFE SCREENING FOR SPARSE REGRESSION WITH THE KULLBACK-LEIBLER DIVERGENCE
- Log in to post comments
Safe screening rules are powerful tools to accelerate iterative solvers in sparse regression problems. They allow early identification of inactive coordinates (i.e., those not belonging to the support of the solution) which can thus be screened out in the course of iterations. In this paper, we extend the GAP Safe screening rule to the L1-regularized Kullback-Leibler divergence which does not fulfill the regularity assumptions made in previous works. The proposed approach is experimentally validated on synthetic and real count data sets.
- Categories:
 68 Views
68 Views
- Read more about MILLIMETER WAVE MIMO CHANNEL ESTIMATION WITH 1-BIT SPATIAL SIGMA-DELTA ANALOG-TO-DIGITAL CONVERTERS
- Log in to post comments
This paper focuses on channel estimation for mmWave MIMO systems with 1-bit spatial sigma-delta analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) and digital-to-analog converters (DACs). The channel estimation performance with 1-bit spatial sigma-delta modulators (i.e., ADCs or DACs) depends on the quantization noise modeling. Therefore, we present a new method for modeling the quantization noise by leveraging the deterministic input-output relation of the 1-bit spatial sigma-delta modulator.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views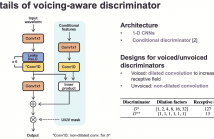
- Read more about Parallel waveform synthesis based on generative adversarial networks with voicing-aware conditional discriminators
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes voicing-aware conditional discriminators for Parallel WaveGAN-based waveform synthesis systems. In this framework, we adopt a projection-based conditioning method that can significantly improve the discriminator's performance. Furthermore, the conventional discriminator is separated into two waveform discriminators for modeling voiced and unvoiced speech.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about Identification of Uterine Contractions by An Ensemble of Gaussian Processes
- Log in to post comments
Identifying uterine contractions with the aid of machine learning methods is necessary vis-á-vis their use in combination with fetal heart rates and other clinical data for the assessment of a fetus wellbeing. In this paper, we study contraction identification by processing noisy signals due to uterine activities. We propose a complete four-step method where we address the imbalanced classification problem with an ensemble Gaussian process classifier, where the Gaussian process latent variable model is used as a decision-maker.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Class-imbalanced classifiers using ensembles of Gaussian processes and Gaussian process latent variable models
- Log in to post comments
Classification with imbalanced data is a common and challenging problem in many practical machine learning problems. Ensemble learning is a popular solution where the results from multiple base classifiers are synthesized to reduce the effect of a possibly skewed distribution of the training set. In this paper, binary classifiers based on Gaussian processes are chosen as bases for inferring the predictive distributions of test latent variables. We apply a Gaussian process latent variable model where the outputs of the Gaussian processes are used for making the final decision.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about Antenna Selection For Massive MIMO Systems Based On POMDP Framework
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 12 Views
12 Views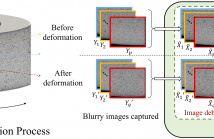
- Read more about FUSION-BASED DIGITAL IMAGE CORRELATION FRAMEWORKFOR STRAIN MEASUREMENT
- Log in to post comments
We address the problem of enabling two-dimensional digital image correlation (DIC) for strain measurement on large three-dimensional objects with curved surfaces. It is challenging to acquire full-field qualified images of the surface required by DIC due to geometric distortion and the narrow visual field of the surface that a single image can cover. To overcome this issue, we propose an end-to-end DIC framework incorporating the image fusion principle to achieve full-field strain measurement over the curved surface.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
Automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems are highly sensitive to train-test domain mismatch. However, because transcription is often prohibitively expensive, it is important to be able to make use of available transcribed out-of-domain data. We address the problem of domain adaptation with semi-supervised training (SST). Contrary to work in in-domain SST, we find significant performance improvement even with just one hour of target-domain data—though, the selection of the data is critical.
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views