
ICASSP 2021 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2021 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about MaskCycleGAN-VC: Learning Non-parallel Voice Conversion with Filling in Frames
- Log in to post comments
This work is concerned with non-parallel voice conversion. In particular, motivated by the recent advances in mel-spectrogram-based vocoders, we focus on conversions in the mel-spectrogram domain based on CycleGAN. The challenge is how to make the converter able to convert only the voice factors while retaining the linguistic content factors that underlie input mel-spectrograms. To solve this, we propose MaskCycleGAN-VC, which is an extension of CycleGAN-VC2 and is trained using a novel auxiliary task called filling in frames (FIF). With FIF, we apply a temporal mask to the input mel-spectrogram and encourage the converter to fill in missing frames based on surrounding frames. This task allows the converter to learn time-frequency structures in a self-supervised manner. A subjective evaluation of the naturalness and speaker similarity showed that MaskCycleGAN-VC outperformed previous CycleGAN-VCs.
- Categories:
 53 Views
53 Views
- Read more about Attention-Embedded Decomposed Network with Unpaired CT Images Prior for Metal Artifact Reduction
- Log in to post comments
Recently, unsupervised learning is proposed to avoid the performance degrading caused by synthesized paired computed tomography (CT) images. However, existing unsupervised methods for metal artifact reduction (MAR) only use features in image space, which is not enough to restore regions heavily corrupted by metal artifacts. Besides, they lack the distinction and selection for effective features. To address these issues, we propose an attention-embedded decomposed network to reduce metal artifacts in both image space and sinogram space with unpaired images.
poster2.pdf
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) often rely on GPS for navigation. GPS signals, however, are very low in power and easily jammed or otherwise disrupted. This paper presents a method for determining the navigation errors present at the beginning of a GPS-denied period utilizing data from a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system. This is accomplished by comparing an online-generated SAR image with a reference image obtained a priori.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) often rely on GPS for navigation. GPS signals, however, are very low in power and easily jammed or otherwise disrupted. This paper presents a method for determining the navigation errors present at the beginning of a GPS-denied period utilizing data from a synthetic aperture radar (SAR) system. This is accomplished by comparing an online-generated SAR image with a reference image obtained a priori.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views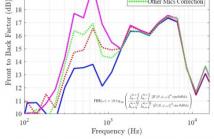
- Read more about Reducing Modal Error Propagation Through Correcting Mismatched Microphone Gains Using RAPID
- Log in to post comments
Microphone array calibration is required to accurately capture the information in an audio source recording. Existing calibration methods require expensive hardware and setup procedures to compute filters for correcting microphone responses. Typically, such methods struggle to extend measurement accuracy to low frequencies. As a result, the error due to microphone gain mismatch propagates to all the modes in the spherical harmonic domain representation of a signal.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about INTEGRATED GRAD-CAM: SENSITIVITY-AWARE VISUAL EXPLANATION OF DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORKS VIA INTEGRATED GRADIENT-BASED SCORING
- Log in to post comments
Visualizing the features captured by Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) is one of the conventional approaches to interpret the predictions made by these models in numerous image recognition applications. Grad-CAM is a popular solution that provides such a visualization by combining the activation maps obtained from the model.However, the average gradient-based terms deployed in this method under-estimates the contribution of the representations discovered by the model to its predictions.
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about ADA-SISE: ADAPTIVE SEMANTIC INPUT SAMPLING FOR EFFICIENT EXPLANATION OF CONVOLUTIONAL NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
Explainable AI (XAI) is an active research area to interpret a neural network’s decision by ensuring transparency and trust in the task-specified learned models.Recently,perturbation-based model analysis has shown better interpretation, but back-propagation techniques are still prevailing because of their computational efficiency. In this work, we combine both approaches as a hybrid visual explanation algorithm and propose an efficient interpretation method for convolutional neural networks.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about Ultrasound elasticity imaging using physics-based models and learning-based plug-and-play priors
- Log in to post comments
Existing physical model-based imaging methods for ultrasound elasticity reconstruction utilize fixed variational regularizers that may not be appropriate for the application of interest or may not capture complex spatial prior information about the underlying tissues. On the other hand, end-to-end learning-based methods count solely on the training data, not taking advantage of the governing physical laws of the imaging system.
ICASSP_slides.pdf
ICASSP_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about AN ATTENTION MODEL FOR HYPERNASALITY PREDICTION IN CHILDREN WITH CLEFT PALATE
- Log in to post comments
Hypernasality refers to the perception of abnormal nasal resonances in vowels and voiced consonants. Estimation of hypernasality severity from connected speech samples involves learning a mapping between the frame-level features and utterance-level clinical ratings of hypernasality. However, not all speech frames contribute equally to the perception of hypernasality.
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views