
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2020 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.

- Read more about Transformer-based text-to-speech with weighted forced attention
- Log in to post comments
This paper investigates state-of-the-art Transformer- and FastSpeech-based high-fidelity neural text-to-speech (TTS) with full-context label input for pitch accent languages. The aim is to realize faster training than conventional Tacotron-based models. Introducing phoneme durations into Tacotron-based TTS models improves both synthesis quality and stability.
- Categories:
 290 Views
290 Views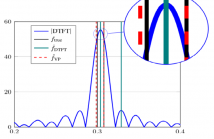
The estimation of the frequencies of multiple complex sinusoids in the presence of noise is required in many applications such as sonar, speech processing, communications, and power systems. This problem can be reformulated as a separable nonlinear least squares problem (SNLLS). In this paper, such formulation is derived and a variable projection (VP) optimization is proposed for solving the SNLLS problem and estimate the frequency parameters. We also apply a lethargy type theorem for quantifying the difficulty of the optimization.
- Categories:
 48 Views
48 Views
- Read more about Robust Transmission over Channels with Channel Uncertainty: An Algorithmic Perspective
- Log in to post comments
The availability and quality of channel state information heavily influences the performance of wireless communication systems. For perfect channel knowledge, optimal signal processing and coding schemes are well studied and often closed-form solutions are known. On the other hand, the case of imperfect channel information is much less understood and closed-form solutions remain unknown in general.
- Categories:
 78 Views
78 Views
- Read more about Small energy masking for improved neural network training for end-to-end speech recognition
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present a Small Energy Masking (SEM) algorithm, which masks inputs having values below a certain threshold. More specifically, a time-frequency bin is masked if the filterbank energy in this bin is less than a certain energy threshold. A uniform distribution is employed to randomly generate the ratio of this energy threshold to the peak filterbank energy of each utterance in decibels. The unmasked feature elements are scaled so that the total sum of the feature values remain the same through this masking procedure.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views
- Read more about Low-complexity and Reliable Transforms for Physical Unclonable Functions
- Log in to post comments
Noisy measurements of a physical unclonable function (PUF) are used to store secret keys with reliability, security, privacy, and complexity constraints. A new set of low-complexity and orthogonal transforms with no multiplication is proposed to obtain bit-error probability results significantly better than all methods previously proposed for key binding with PUFs. The uniqueness and security performance of a transform selected from the proposed set is shown to be close to optimal.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Robust speaker recognition using unsupervised adversarial invariance
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of speaker recognition in challenging acoustic conditions using a novel method to extract robust speaker-discriminative speech representations. We adopt a recently proposed unsupervised adversarial invariance architecture to train a network that maps speaker embeddings extracted using a pre-trained model onto two lower dimensional embedding spaces. The embedding spaces are learnt to disentangle speaker-discriminative information from all other information present in the audio recordings, without supervision about the acoustic conditions.
- Categories:
 56 Views
56 Views
- Read more about Robust speaker recognition using unsupervised adversarial invariance
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we address the problem of speaker recognition in challenging acoustic conditions using a novel method to extract robust speaker-discriminative speech representations. We adopt a recently proposed unsupervised adversarial invariance architecture to train a network that maps speaker embeddings extracted using a pre-trained model onto two lower dimensional embedding spaces. The embedding spaces are learnt to disentangle speaker-discriminative information from all other information present in the audio recordings, without supervision about the acoustic conditions.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
This paper presents a domain adaptation model for sound event detection. A common challenge for sound event detection is how to deal with the mismatch among different datasets. Typically, the performance of a model will decrease if it is tested on a dataset which is different from the one that the model is trained on. To address this problem, based on convolutional recurrent neural networks (CRNNs), we propose an adapted CRNN (A-CRNN) as an unsupervised adversarial domain adaptation model for sound event detection.
- Categories:
 115 Views
115 Views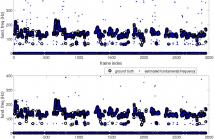
Most parametric fundamental frequency estimators make the implicit assumption that any corrupting noise is additive, white Gaussian. Under this assumption, the maximum likelihood (ML) and the least squares estimators are the same, and statistically efficient. However, in the coloured noise case, the estimators differ, and the spectral shape of the corrupting noise should be taken into account.
- Categories:
 158 Views
158 Views
- Read more about Feature Affine Projection Algorithms
- Log in to post comments
There is a growing research interest in proposing new techniques to detect and exploit signals/systems sparsity. Recently, the idea of hidden sparsity has been proposed, and it has been shown that, in many cases, sparsity is not explicit, and some tools are required to expose hidden sparsity. In this paper, we propose the Feature Affine Projection (F-AP) algorithm to reveal hidden sparsity in unknown systems. Indeed, first, the hidden sparsity is revealed using the feature matrix, then it is exploited using some sparsity-promoting penalty function.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views