
ICASSP is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2020 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit website.
- Read more about RAW WAVEFORM BASED END-TO-END DEEP CONVOLUTIONAL NETWORK FOR SPATIAL LOCALIZATION OF MULTIPLE ACOUSTIC SOURCES
- Log in to post comments
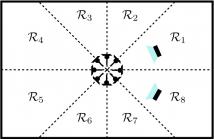
In this paper, we present an end-to-end deep convolutional neural network operating on multi-channel raw audio data to localize multiple simultaneously active acoustic sources in space. Previously reported end-to-end deep learning based approaches work well in localizing a single source directly from multi-channel raw-audio, but are not easily extendable to localize multiple sources due to the well known permutation problem.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views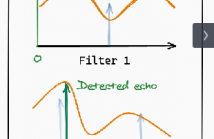
- Read more about BLASTER: An off-grid method for blind and regularized acoustic echoes retrieval
- Log in to post comments
Acoustic echoes retrieval is a research topic that is gaining importance in many speech and audio signal processing applications such as speech enhancement, source separation, dereverberation and room geometry estimation. This work proposes a novel approach to blindly retrieve the off-grid timing of early acoustic echoes from a stereophonic recording of an unknown sound source such as speech. It builds on the recent framework of continuous dictionaries.
- Categories:
 97 Views
97 Views
- Read more about Accelerating Linear Algebra Kernels on a Massively Parallel Reconfigurable Architecture
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 229 Views
229 Views
- Read more about A Hybrid Approach for Thermographic Imaging with Deep Learning
- Log in to post comments
We propose a hybrid method for reconstructing thermographic images by combining the recently developed virtual wave concept with deep neural networks. The method can be used to detect defects inside materials in a non-destructive way. We propose two architectures along with a thorough evaluation that shows a substantial improvement compared to state-of-the-art reconstruction procedures. The virtual waves are invariant of the thermal diffusivity property of the material.
- Categories:
 88 Views
88 Views
- Read more about Two-Step Sound Source Separation: Training on Learned Latent Targets (Presentation)
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a two-step training procedure for source separation via a deep neural network. In the first step we learn a transform (and it's inverse) to a latent space where masking-based separation performance using oracles is optimal. For the second step, we train a separation module that operates on the previously learned space. In order to do so, we also make use of a scale-invariant signal to distortion ratio (SI-SDR) loss function that works in the latent space, and we prove that it lower-bounds the SI-SDR in the time domain.
- Categories:
 400 Views
400 Views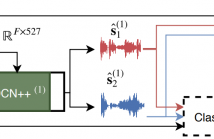
- Read more about Improving Universal Sound Separation Using Sound Classification Presentation
- Log in to post comments
Deep learning approaches have recently achieved impressive performance on both audio source separation and sound classification. Most audio source separation approaches focus only on separating sources belonging to a restricted domain of source classes, such as speech and music. However, recent work has demonstrated the possibility of "universal sound separation", which aims to separate acoustic sources from an open domain, regardless of their class.
- Categories:
 428 Views
428 Views- Read more about Environment-aware Reconfigurable Noise Suppression
- Log in to post comments
The paper proposes an efficient, robust, and reconfigurable technique to suppress various types of noises for any sampling rate. The theoretical analyses, subjective and objective test results show that the proposed noise suppression (NS) solution significantly enhances the speech transmission index (STI), speech intelligibility (SI), signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), and subjective listening experience. The STI and SI consists of 5 levels, i.e., bad, poor, fair, good, and excellent. The most common noisy condition is of SNR ranging from -5 to 8 dB.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views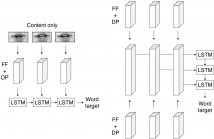
We present a novel lipreading system that improves on the task of speaker-independent word recognition by decoupling motion and content dynamics. We achieve this by implementing a deep learning architecture that uses two distinct pipelines to process motion and content and subsequently merges them, implementing an end-to-end trainable system that performs fusion of independently learned representations. We obtain a average relative word accuracy improvement of ≈6.8% on unseen speakers and of ≈3.3% on known speakers, with respect to a baseline which uses a standard architecture.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views
The enhancement of noisy speech is important for applications involving human-to-human interactions, such as telecommunications and hearing aids, as well as human-to-machine interactions, such as voice-controlled systems and robot audition. In this work, we focus on reverberant environments. It is shown that, by exploiting the lack of correlation between speech and the late reflections, further noise reduction can be achieved. This is verified using simulations involving actual acoustic impulse responses and noise from the ACE corpus.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views
- Read more about END-TO-END ARTICULATORY MODELING FOR DYSARTHRIC ARTICULATORY ATTRIBUTE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
In this study, we focus on detecting articulatory attribute errors for dysarthric patients with cerebral palsy (CP) or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). There are two major challenges for this task. The pronunciation of dysarthric patients is unclear and inaccurate, which results in poor performances of traditional automatic speech recognition (ASR) systems and traditional automatic speech attribute transcription (ASAT). In addition, the data is limited because of the difficulty of recording.
- Categories:
 42 Views
42 Views