
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
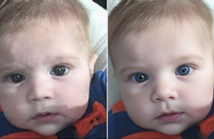
Presentation attacks on biometric systems have long created significant security risks. The increase in the adoption of age verification systems, which ensure that only age-appropriate content is consumed online, raises the question of vulnerability of such systems to replay presentation attacks. In this paper, we analyze the vulnerability of face age verification to simple replay attacks and assess whether presentation attack detection (PAD) systems created for biometrics can be effective at detecting similar attacks on age verification.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about CORN: Co-Trained Full- And No-Reference Speech Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Perceptual evaluation constitutes a crucial aspect of various audio-processing tasks. Full reference (FR) or similarity-based metrics rely on high-quality reference recordings, to which lower-quality or corrupted versions of the recording may be compared for evaluation. In contrast, no-reference (NR) metrics evaluate a recording without relying on a reference. Both the FR and NR approaches exhibit advantages and drawbacks relative to each other.
2310.09388.pdf
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Joint Signal Recovery and Graph Learning from Incomplete Time-Series
- Log in to post comments
Learning a graph from data is the key to taking advantage of graph signal processing tools. Most of the conventional algorithms for graph learning require complete data statistics, which might not be available in some scenarios. In this work, we aim to learn a graph from incomplete time-series observations. From another viewpoint, we consider the problem of semi-blind recovery of time-varying graph signals where the underlying graph model is unknown.
- Categories:
 65 Views
65 Views
- Read more about A Parameterized Generative Adversarial Network Using Cyclic Projection for Explainable Medical Image Classification
- Log in to post comments
Although current data augmentation methods are successful to alleviate the data insufficiency, conventional augmentation are primarily intra-domain while advanced generative adversarial networks (GANs) generate images remaining uncertain, particularly in small-scale datasets. In this paper, we propose a parameterized GAN (ParaGAN) that effectively controls the changes of synthetic samples among domains and highlights the attention regions for downstream classification.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views
- Read more about LOW COST VARIABLE STEP-SIZE LMS WITH MAXIMUM SIMILARITY TO THE AFFINE PROJECTION ALGORITHM
- Log in to post comments
The LMS algorithm is widely employed in adaptive systems due to its robustness, simplicity, and reasonable performance. However, it is well known that this algorithm suffers from a slow convergence speed when dealing with colored reference signals. Numerous variants and alternative algorithms have been proposed to address this issue, though all of them entail an increase in computational cost. Among the proposed alternatives, the affine projection algorithm stands out. This algorithm has the peculiarity of starting from N data vectors of the reference signal.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Self-supervised Speaker Verification Employing a Novel Clustering Algorithm
- Log in to post comments
Clustering is an unsupervised learning technique, which leverages a large amount of unlabeled data to learn cluster-wise representations from speech. One of the most popular self-supervised techniques to train a speaker verification system is to predict the pseudo-labels using clustering algorithms and then train the speaker embedding network using the generated pseudo-labels in a discriminative manner. Therefore, pseudo-labels - driven self-supervised speaker verification systems' performance relies heavily on the accuracy of the adopted clustering algorithms.
- Categories:
 84 Views
84 Views
The widespread adoption of smartphones has introduced new challenges to document copyright protection, prompting the emergence of Screen-Shooting Resilient Document Watermarking (SSRDW) technology. In recent years, underpainting-based SSRDW techniques have proven to be highly effective. However, after careful study, we find that existing methods fail to simultaneously meet four essential criteria for SSRDW: high imperceptibility, strong
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about FastGAT: Simple and Efficient Graph Attention Neural Network with Global-aware Adaptive Computational Node Attention
- Log in to post comments
Graph attention neural network (GAT) stands as a fundamental model within graph neural networks, extensively employed across various applications. It assigns different weights to different nodes for feature aggregation by comparing the similarity of features between nodes. However, as the amount and density of graph data increases, GAT's computational demands rise steeply. In response, we present FastGAT, a simpler and more efficient graph attention neural network with global-aware adaptive computational node attention.
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about ADAPTIVE VIDEO WATERMARKING WITH PERCEPTUAL GUARANTEE AND EFFICIENCY OPTIMIZATION
- Log in to post comments
Existing video watermarking embeds robust watermarks in each frame of the video for copyright protection and tracking. However, just as any content written on a blank paper is easily perceived, embedding watermarks in the texture-poor frames impairs imperceptibility. Common geometric attacks such as scaling and rotation pose a significant challenge to the existing video watermarking. Image watermarking based on moments is robust against geometric attacks.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 Views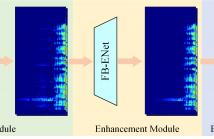
- Read more about RENet: A Time-Frequency Domain General Speech Restoration Network for ICASSP 2024 Speech Signal Improvement Challenge
- Log in to post comments
The ICASSP 2024 Speech Signal Improvement (SSI) Challenge seeks to address speech quality degradation problems in telecommunication systems. In this context, this paper proposes RENet, a time-frequency (T-F) domain method leveraging complex spectrum mapping to mitigate speech distortions. Specifically, the proposed RENet is a multi-stage network. First, TF-GridGAN was designed to recover the degraded speech with a generative adversarial network (GAN). Second, a full-band enhancement module was introduced to eliminate residual noises and artifacts existed in the output of TF-GridGAN.
2024.4.19.pptx
- Categories:
 240 Views
240 Views