
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about 3D POSE ESTIMATION FROM MONOCULAR VIDEO WITH CAMERA-BONE ANGLE REGULARIZATION ON THE IMAGE FEATURE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a monocular 3D pose estimation method which explicitly takes into account the angles between the camera optical axis and bones (camera-bone angles) as well as temporal information. The proposed method combines a 2D-to-3D-based method, which predicts a 3D pose from a sequence of 2D poses, and convolutional neural network (CNN) and includes novel regularization loss to enable the CNN to extract camera-bone-angle information.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views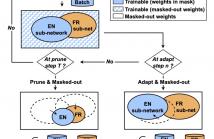
- Read more about Dynamic ASR pathways: An Adaptive Masking Approach Towards Efficient Pruning of a Multilingual ASR Model
- Log in to post comments
Neural network pruning offers an effective method for compressing a multilingual automatic speech recognition (ASR) model with minimal performance loss. However, it entails several rounds of pruning and re-training needed to be run for each language. In this work, we propose the use of an adaptive masking approach in two scenarios for pruning a multilingual ASR model efficiently, each resulting in sparse monolingual models or a sparse multilingual model (named as Dynamic ASR Pathways).
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views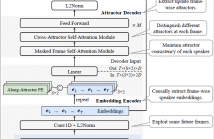
- Read more about Frame-wise streaming end-to-end speaker diarization with non-autoregressive self-attention-based attractors
- Log in to post comments
This work proposes a frame-wise online/streaming end-to-end neural diarization (FS-EEND) method in a frame-in-frame-out fashion. To frame-wisely detect a flexible number of speakers and extract/update their corresponding attractors, we propose to leverage a causal speaker embedding encoder and an online non-autoregressive self-attention-based attractor decoder. A look-ahead mechanism is adopted to allow leveraging some future frames for effectively detecting new speakers in real time and adaptively updating speaker attractors.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about LEVERAGING EFFECTIVE LANGUAGE AND SPEAKER CONDITIONING IN INDIC TTS FOR LIMMITS 2024 CHALLENGE
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we explain the model that was developed by the NLP\_POSTECH team for the LIMMITS 2024 Grand Challenge. Among the three tracks, we focus on Track 1, which necessitates the creation of a few-shot text-to-speech (TTS) system that generates natural speech across diverse languages. Towards this end, to realize multi-lingual capability, we incorporate a learnable language embedding. In addition, for precise imitation of target speaker voices, we leverage an inductive speaker bias conditioning methodology.
- Categories:
 25 Views
25 Views
- Read more about External Division of Two Proximity Operators: An Application to Signal Recovery with Structured Sparsity
- Log in to post comments
This paper studies the external division operator, an external division (an affine combination with positive and negative weights) of two proximity operators. We show that the external division operator is cocoercive under some condition, and it can be expressed as the proximity operator of a certain weakly convex function. We then consider using the external division operator as an alternative to the proximity operator in the proximal gradient algorithm, which we show converges to a minimizer of the cost function penalized by the weakly convex function under some conditions.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about ”IT IS OKAY TO BE UNCOMMON”: QUANTIZING SOUND EVENT DETECTION NETWORKS ON HARDWARE ACCELERATORS WITH UNCOMMON SUB-BYTE SUPPORT
- Log in to post comments
If our noise-canceling headphones can understand our audio environments, they can then inform us of important sound events, tune equalization based on the types of content we listen to, and dynamically adjust noise cancellation parameters based on audio scenes to further reduce distraction. However, running multiple audio understanding models on headphones with a limited energy budget and on-chip memory remains a challenging task.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views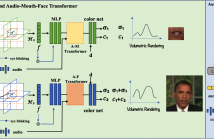
- Read more about DT-NeRF: Decomposed Triplane-Hash Neural Radiance Fields for High-Fidelity Talking Portrait Synthesis
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present the decomposed triplane-hash neural radiance fields (DT-NeRF), a framework that significantly improves the photorealistic rendering of talking faces and achieves state-of-the-art results on key evaluation datasets. Our architecture decomposes the facial region into two specialized triplanes: one specialized for representing the mouth, and the other for the broader facial features. We introduce audio features as residual terms and integrate them as query vectors into our model through an audio-mouthface transformer.
- Categories:
 35 Views
35 Views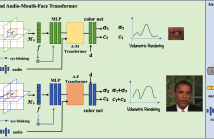
- Read more about DT-NeRF: Decomposed Triplane-Hash Neural Radiance Fields for High-Fidelity Talking Portrait Synthesis
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present the decomposed triplane-hash neural radiance fields (DT-NeRF), a framework that significantly improves the photorealistic rendering of talking faces and achieves state-of-the-art results on key evaluation datasets. Our architecture decomposes the facial region into two specialized triplanes: one specialized for representing the mouth, and the other for the broader facial features. We introduce audio features as residual terms and integrate them as query vectors into our model through an audio-mouthface transformer.
- Categories:
 27 Views
27 Views
- Read more about Enhancing Adversarial Transferability in Object Detection with Bidirectional Feature Distortion
- Log in to post comments
Previous works have shown that perturbing internal-layer features can significantly enhance the transferability of black-box attacks in classifiers. However, these methods have not achieved satisfactory performance when applied to detectors due to the inherent differences in features between detectors and classifiers. In this paper, we introduce a concise and practical untargeted adversarial attack in a label-free manner, which leverages only the feature extracted from the backbone model.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about EXPLORING CONSISTENT SPATIO-TEMPORAL DISTORTION AND STABLE 3-D DCT COEFFICIENTS FOR ROBUST BLIND VIDEO WATERMARKING
- Log in to post comments
With the rapid development of mobile Internet and video applications, robust video watermarking technology has become a focal area of research for protecting and tracking intellectual property rights in digital media. An important characteristic of video is that it has both spatial and temporal properties. Previous studies in video watermarking have primarily focused on either spatial or temporal distortions and did not uniformly consider all types of video distortion, which restricts the robustness of video watermarking.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views