
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.
- Read more about PERFORMANCE CONDITIONING FOR DIFFUSION-BASED MULTI-INSTRUMENT MUSIC SYNTHESIS
- Log in to post comments
Generating multi-instrument music from symbolic music representations is an important task in Music Information Retrieval (MIR). A central but still largely unsolved problem in this context is musically and acoustically informed control in the generation process. As the main contribution of this work, we propose enhancing control of multi-instrument synthesis by conditioning a generative model on a specific performance and recording environment, thus allowing for better guidance of timbre and style.
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Character Attribute Extraction from Movie Scripts using LLMs
- Log in to post comments
Narrative understanding is an integrative task of studying characters, plots, events, and relations in a story.
It involves natural language processing tasks such as named entity recognition and coreference resolution to identify the characters, semantic role labeling and argument mining to find character actions and events, information extraction and question answering to describe character attributes, causal analysis to relate different events, and summarization to find the main storyline.
- Categories:
 92 Views
92 Views
- Read more about THE USTC SYSTEM FOR CADENZA 2024 CHALLENGE
- Log in to post comments
This paper reports our submission to the ICASSP 2024 Cadenza Challenge, focusing on the non-causal system. The challenge aims to develop a signal processing system that enables personalized rebalancing of music to improve the listening experience for individuals with hearing loss when they listen to music via their hearing aids. The system is based on the Hybrid Demucs model. We fine-tuned the baseline model on the given dataset with a multi-target strategy and added a mixture of information in the downmixing stage.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about SCORE CALIBRATION BASED ON CONSISTENCY MEASURE FACTOR FOR SPEAKER VERIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
This paper proposes a new scoring calibration method named ``Consistency-Aware Score Calibration", which introduces a Consistency Measure Factor (CMF) to measure the stability of audio voiceprints in similarity scores for speaker verification. The CMF is inspired by the limitations in segment scoring, where the segments with shorter length are not friendly to calculate the similarity score.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about Quantum Privacy Aggregation of Teacher Ensembles (QPATE) for Privacy-preserving Quantum Machine Learning
- Log in to post comments
The utility of machine learning has rapidly expanded in the last two decades and presented an ethical challenge. Papernot et. al. developed a technique, known as Private Aggregation of Teacher Ensembles (PATE) to enable federated learning in which multiple \emph{distributed teachers} are trained on disjoint data sets. This study is the first to apply PATE to an ensemble of quantum neural networks (QNN) to pave a new way of ensuring privacy in quantum machine learning (QML).
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views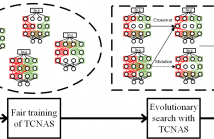
- Read more about TCNAS: TRANSFORMER ARCHITECTURE EVOLVING IN CODE CLONE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Code clone detection aims at finding code fragments with syntactic or semantic similarity. Most of current approaches mainly focus on detecting syntactic similarity while ignoring semantic long-term context alignment, and these detection methods encode the source code using human-designed models, a process which requires both expert input and a significant cost of time for experimentation and refinement. To address these challenges, we introduce the Transformer Code Neural Architecture Search (TCNAS), an approach designed to optimize transformer-based architectures for detection.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views
- Read more about [Slides] Multi-Sensor Multi-Scan Radar Sensing of Multiple Extended Targets
- Log in to post comments
We propose an efficient solution to the state estimation problem in multi-scan multi-sensor multiple extended target sensing scenarios. We first model the measurement process by a doubly inhomogeneous-generalized shot noise Cox process and then estimate the parameters using a jump Markov chain Monte Carlo sampling technique. The proposed approach scales linearly in the number of measurements and can take spatial properties of the sensors into account, herein, sensor noise covariance, detection probability, and resolution.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views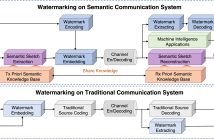
- Read more about SEMANTIC SECURITY: A DIGITAL WATERMARK METHOD FOR IMAGE SEMANTIC PRESERVATION
- Log in to post comments
This is a poster on a proposed watermarking method. In the research, we first chose position vector domain instead of traditional spatial or frequency domain. In addition, we successfully implemented watermarking on semantic communication system. Third, we modeled watermarking channel so that researchers could systematically research watermarking process.
For more information, please check out the publication at IEEE Xplore:
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about DELVING DEEPER INTO VULNERABLE SAMPLES IN ADVERSARIAL TRAINING
- Log in to post comments
Recently, vulnerable samples have been shown to be crucial
for improving adversarial training performance. Our analysis
on existing vulnerable samples mining methods indicate that
existing methods have two problems: 1) valuable connections
among different pairs of natural samples and their adversarial
counterparts are ignored; 2) parts of vulnerable samples are
unconsidered. To better leverage vulnerable samples, we propose INter PAir ConstrainT (INPACT) and Vulnerable Aware
poster(3).pptx
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about CROSS BRANCH FEATURE FUSION DECODER FOR CONSISTENCY REGULARIZATION-BASED SEMI-SUPERVISED CHANGE DETECTION
- Log in to post comments
Semi-supervised change detection (SSCD) utilizes partially labeled data and a large amount of unlabeled data to detect changes. However, the transformer-based SSCD network does not perform as well as the convolution-based SSCD network due to the lack of labeled data. To overcome this limitation, we introduce a new decoder called Cross Branch Feature Fusion (CBFF), which combines the strengths of both local convolutional branch and global transformer branch. The convolutional branch is easy to learn and can produce high-quality features with a small amount of labeled data.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views