- Acoustic Modeling for Automatic Speech Recognition (SPE-RECO)
- General Topics in Speech Recognition (SPE-GASR)
- Large Vocabulary Continuous Recognition/Search (SPE-LVCR)
- Lexical Modeling and Access (SPE-LEXI)
- Multilingual Recognition and Identification (SPE-MULT)
- Resource constrained speech recognition (SPE-RCSR)
- Robust Speech Recognition (SPE-ROBU)
- Speaker Recognition and Characterization (SPE-SPKR)
- Speech Adaptation/Normalization (SPE-ADAP)
- Speech Analysis (SPE-ANLS)
- Speech Coding (SPE-CODI)
- Speech Enhancement (SPE-ENHA)
- Speech Perception and Psychoacoustics (SPE-SPER)
- Speech Production (SPE-SPRD)
- Speech Synthesis and Generation, including TTS (SPE-SYNT)

- Read more about PARALLEL-DATA-FREE DICTIONARY LEARNING FOR VOICE CONVERSION USING NON-NEGATIVE TUCKER DECOMPOSITION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views
- Read more about ON THE IMPORTANCE OF ANALYTIC PHASE OF SPEECH SIGNALS IN SPOKEN LANGUAGE RECOGNITION
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study the role of long-time analytic phase of speech
signals in spoken language recognition (SLR) and employ a set
of features termed as instantaneous frequency cepstral coefficients
(IFCC). We extract IFCC from long-time analytic phase, in an effort
to capture long range acoustic features from speech signals. These
features are used in combination with the traditional shifted delta
cepstral coefficients (SDCC) for SLR. As the SDCC are extracted
from spectral magnitude and IFCC are from analytic phase, they
LRE_poster.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about CROSS-LINGUAL AND MULTILINGUAL SPEECH EMOTION RECOGNITION ON ENGLISH AND FRENCH
- Log in to post comments
poster_final.pdf
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about 3-D CNN Models FOR FAR-FIELD MULTI-CHANNEL Speech Recognition
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about DYNAMIC MULTI-RATER GAUSSIAN MIXTURE REGRESSION INCORPORATING TEMPORAL DEPENDENCIES OF EMOTION UNCERTAINTY USING KALMAN FILTERS
- Log in to post comments
Predicting continuous emotion in terms of affective attrib-utes has mainly been focused on hard labels, which ignored the ambiguity of recognizing certain emotions. This ambigu-ity may result in high inter-rater variability and in turn caus-es varying prediction uncertainty with time. Based on the assumption that temporal dependencies occur in the evolu-tion of emotion uncertainty, this paper proposes a dynamic multi-rater Gaussian Mixture Regression (GMR), aiming to obtain the emotion uncertainty prediction reflected by multi-raters by taking into account their temporal dependencies.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about COMPLEX-VALUED GAUSSIAN PROCESS LATENT VARIABLE MODEL FOR PHASE-INCORPORATING SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Read more about COMPLEX-VALUED GAUSSIAN PROCESS LATENT VARIABLE MODEL FOR PHASE-INCORPORATING SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views
- Read more about AUTOMATIC SPEECH ASSESSMENT FOR APHASIC PATIENTS BASED ON SYLLABLE-LEVEL EMBEDDING AND SUPRA-SEGMENTAL DURATION FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
Aphasia is a type of acquired language impairment resulting from brain injury. Speech assessment is an important part of the comprehensive assessment process for aphasic patients. It is based on the acoustical and linguistic analysis of patients’ speech elicited through pre-defined story-telling tasks. This type of narrative spontaneous speech embodies multi-fold atypical characteristics related to the underlying language impairment.
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views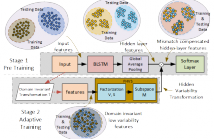
- Read more about FACTORIZED HIDDEN VARIABILITY LEARNING FOR ADAPTATION OF SHORT DURATION LANGUAGE IDENTIFICATION MODELS
- Log in to post comments
Bidirectional long short term memory (BLSTM) recurrent neural networks (RNNs) have recently outperformed other state-of-the-art approaches, such as i-vector and deep neural networks (DNNs) in automatic language identification (LID), particularly when testing with very short utterances (∼3s). Mismatches conditions between training and test data, e.g. speaker, channel, duration and environmental noise, are a major source of performance degradation for LID.
POSTER.pdf
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views