
IEEE ICASSP 2023 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The ICASSP 2023 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views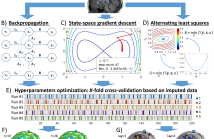
- Read more about DYNAMIC SOURCE LOCALIZATION AND FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY ESTIMATION WITH STATE-SPACE MODELS: PRELIMINARY FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS - Preprint and Code
- Log in to post comments
Dynamic imaging of source and functional connectivity (FC) using electroencephalographic (EEG) signals is essential for understanding the brain and cognition with sufficiently affordable technology to be widely applicable for studying changes associated with healthy ageing and the progression of neuropathology. We present an application for group analysis of recently developed state-space models and algorithms for simultaneously estimating the large-scale EEG inverse and FC problems.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views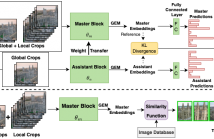
- Read more about MABNet: Master Assistant Buddy Network with Hybrid Learning for Image Retrieval
- Log in to post comments
Image retrieval has garnered a growing interest in recent times. The current approaches are either supervised or self-supervised. These methods do not exploit the benefits of hybrid learning using both supervision and self-supervision. We present a novel Master Assistant Buddy Network (MABNet) for image retrieval which incorporates both the learning mechanisms. MABNet consists of master and assistant block, both learning independently through supervision and collectively via self-supervision.
MABNET_ICASSP (6).pdf
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Reducing the Communication and Computational Cost of Random Fourier Features Kernel LMS in Diffusion Networks
- Log in to post comments
Diffusion kernel algorithms are interesting tools for distributed nonlinear estimation. However, for the sake of feasibility, it is essential in practice to restrict their computational cost and the number of communications. In this paper, we propose a censoring algorithm for adaptive kernel diffusion networks based on random Fourier features that locally adapts the number of nodes censored according to the estimation error.
- Categories:
 23 Views
23 Views
- Read more about DYNAMIC SOURCE LOCALIZATION AND FUNCTIONAL CONNECTIVITY ESTIMATION WITH STATE-SPACE MODELS: PRELIMINARY FEASIBILITY ANALYSIS - Poster and Video
- Log in to post comments
Dynamic imaging of source and functional connectivity (FC) using electroencephalographic (EEG) signals is essential for understanding the brain and cognition with sufficiently affordable technology to be widely applicable for studying changes associated with healthy ageing and the progression of neuropathology. We present an application for group analysis of recently developed state-space models and algorithms for simultaneously estimating the large-scale EEG inverse and FC problems.
- Categories:
 116 Views
116 Views
- Read more about SPEECH-BASED EMOTION RECOGNITION WITH SELF-SUPERVISED MODELS USING ATTENTIVE CHANNEL-WISE CORRELATIONS AND LABEL SMOOTHING
- Log in to post comments
When recognizing emotions from speech, we encounter two common problems: how to optimally capture emotion-relevant information from the speech signal and how to best quantify or categorize the noisy subjective emotion labels. Self-supervised pre-trained representations can robustly capture information from speech enabling state-of-the-art results in many downstream tasks including emotion recognition. However, better ways of aggregating the information across time need to be considered as the relevant emotion information is likely to appear piecewise and not uniformly across the signal.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views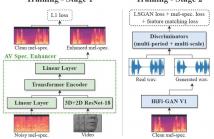
- Read more about LA-VocE: Low-SNR Audio-visual Speech Enhancement using Neural Vocoders
- Log in to post comments
Audio-visual speech enhancement aims to extract clean speech from a noisy environment by leveraging not only the audio itself but also the target speaker's lip movements. This approach has been shown to yield improvements over audio-only speech enhancement, particularly for the removal of interfering speech. Despite recent advances in speech synthesis, most audio-visual approaches continue to use spectral mapping/masking to reproduce the clean audio, often resulting in visual backbones added to existing speech enhancement architectures.
- Categories:
 38 Views
38 Views
- Read more about Residual Squeeze-and-Excitation U-shaped Network for Minutia Extraction in Contactless Fingerprint Images
- Log in to post comments
Slides.pdf
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Fast Robust Principle Component Analysis using Gauss-Newton Iterations
- Log in to post comments
Robust Principal Component Analysis (RPCA) is an optimization problem that decomposes a data matrix into a low-rank and a sparse matrix. However, solving this problem using alternating procedures requires sequentially computing singular value decompositions (SVDs) of large matrices, which is computationally expensive. In this work, we propose a computation protocol that leverages Gauss-Newton iterations to speed up the sequential computation of SVDs and accelerate the entire RPCA process.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views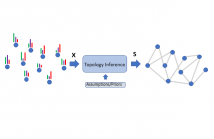
- Read more about Network Topology Inference from Gaussian and Stationary Graph Signals
- Log in to post comments
Graphs have become pervasive tools to represent information and datasets with irregular support. However, in many cases, the underlying graph is either unavailable or naively obtained, calling for more advanced methods for its estimation. Indeed, graph topology inference methods that estimate the network structure from a set of signal observations have a long and well-established history. By assuming that the observations are both Gaussian and stationary in the sought graph, this paper proposes a new scheme to learn the network from nodal observations.
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views