- Signal and System Modeling, Representation and Estimation
- Multirate Signal Processing
- Sampling and Reconstruction
- Nonlinear Systems and Signal Processing
- Filter Design
- Adaptive Signal Processing
- Statistical Signal Processing

- Read more about EXPLORING DEEPER GRAPH CONVOLUTIONS FOR SEMI-SUPERVISED NODE CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 14 Views
14 Views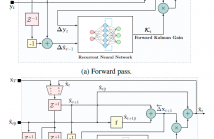
- Read more about RTSNET: DEEP LEARNING AIDED KALMAN SMOOTHING
- Log in to post comments
The smoothing task is the core of many signal processing applications. It deals with the recovery of a sequence of hidden state variables from a sequence of noisy observations in a one-shot manner. In this work we propose RTSNet, a highly efficient model-based and data-driven smoothing algorithm. RTSNet integrates dedicated trainable models into the flow of the classical Rauch-Tung-Striebel (RTS) smoother, and is able to outperform it when operating under model mismatch and non-linearities while retaining its efficiency and interpretability.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about SCREEN & RELAX: ACCELERATING THE RESOLUTION OF ELASTIC-NET BY SAFE IDENTIFICATION OF THE SOLUTION SUPPORT
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a procedure to accelerate the resolution of the well-known ``Elastic-Net'' problem. Our procedure is based on the (partial) identification of the solution support and the reformulation of the original problem into a problem of reduced dimension. The identification of the support leverages the novel concept of ``safe relaxing'' where one aims to identify non-zero coefficients of the solution.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about SCREEN & RELAX: ACCELERATING THE RESOLUTION OF ELASTIC-NET BY SAFE IDENTIFICATION OF THE SOLUTION SUPPORT
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we propose a procedure to accelerate the resolution of the well-known ``Elastic-Net'' problem. Our procedure is based on the (partial) identification of the solution support and the reformulation of the original problem into a problem of reduced dimension. The identification of the support leverages the novel concept of ``safe relaxing'' where one aims to identify non-zero coefficients of the solution.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 7 Views
7 Views
- Read more about NODE-SCREENING TESTS FOR THE L0-PENALIZED LEAST-SQUARES PROBLEM
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel screening methodology to safely discard irrelevant nodes within a generic branch-and-bound (BnB) algorithm solving the l0-penalized least-squares problem. Our contribution is a set of two simple tests to detect sets of feasible vectors that cannot yield optimal solutions. This allows to prune nodes of the BnB search tree, thus reducing the overall optimization time. One cornerstone of our contribution is a nesting property between tests at different nodes that allows to implement them with a low computational cost.
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about NODE-SCREENING TESTS FOR THE L0-PENALIZED LEAST-SQUARES PROBLEM
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel screening methodology to safely discard irrelevant nodes within a generic branch-and-bound (BnB) algorithm solving the l0-penalized least-squares problem. Our contribution is a set of two simple tests to detect sets of feasible vectors that cannot yield optimal solutions. This allows to prune nodes of the BnB search tree, thus reducing the overall optimization time. One cornerstone of our contribution is a nesting property between tests at different nodes that allows to implement them with a low computational cost.
slides.pdf
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about Fast and Stable Convergence of Online SGD for CV@R-based Risk-Aware Statistical Learning
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views


- Read more about Sparse time-frequency representation via atomic norm minimization
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views