
IEEE ICASSP 2024 - IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP) is the world’s largest and most comprehensive technical conference focused on signal processing and its applications. The IEEE ICASSP 2024 conference will feature world-class presentations by internationally renowned speakers, cutting-edge session topics and provide a fantastic opportunity to network with like-minded professionals from around the world. Visit the website.

- Read more about SPIKING STRUCTURED STATE SPACE MODEL FOR MONAURAL SPEECH ENHANCEMENT
- Log in to post comments
Speech enhancement seeks to extract clean speech from noisy signals. Traditional deep learning methods face two challenges: efficiently using information in long speech sequences and high computational costs. To address these, we introduce the Spiking Structured State Space Model (Spiking-S4). This approach merges the energy efficiency of Spiking Neural Networks (SNN) with the long-range sequence modeling capabilities of Structured State Space Models (S4), offering a compelling solution.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views
- Read more about TD-GPT: Target Protein-Specific Drug Molecule Generation GPT
- Log in to post comments
Drug discovery faces challenges due to the vast chemical space and complex drug-target interactions. This paper proposes a novel deep learning framework TD-GPT for targeted drug molecule generation. TD-GPT comprises a linear Transformer for drug-target affinity prediction, an affinity-enhanced protein encoder using sequences, and a target-specific attention module in the molecular Transformer decoder. Experiments demonstrate TD-GPT’s efficiency in generating valid, novel molecules with high affinity and specificity for desired targets without target fine-tuning.
- Categories:
 45 Views
45 Views
- Read more about A graph-prediction-based approach for debiasing underreported data
- Log in to post comments
We present a novel Graph-based debiasing Algorithm for Underreported Data (GRAUD) aiming at an efficient joint estimation of event counts and discovery probabilities across spatial or graphical structures. This innovative method provides a solution to problems seen in fields such as policing data and COVID-19 data analysis. Our approach avoids the need for strong priors typically associated with Bayesian frameworks. By leveraging the graph structures on unknown variables n and p, our method debiases the under-report data and estimates the discovery probability at the same time.
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views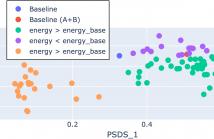
- Read more about Performance And Energy Balance: A Comprehensive Study Of State-Of-The-Art Sound Event Detection Systems - Poster
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, deep learning systems have shown a concerning trend toward increased complexity and higher energy consumption. As researchers in this domain and organizers of one of the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events challenges task, we recognize the importance of addressing the environmental impact of data-driven SED systems. In this paper, we propose an analysis focused on SED systems based on the challenge submissions. This includes a comparison across the past two years and a detailed analysis of this year’s SED systems.
- Categories:
 32 Views
32 Views
- Read more about MAXIMUM LIKELIHOOD-BASED GRIDLESS DOA ESTIMATION USING STRUCTURED COVARIANCE MATRIX RECOVERY AND SBL WITH GRID REFINEMENT
- Log in to post comments
We consider the parametric measurement model employed in applications such as line spectral or direction-of-arrival estimation with the goal to estimate the underlying parameter in a gridless manner. We focus on the stochastic maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) framework and overcome the model complexities of the past by reparameterization of the objective and exploiting the sparse Bayesian learning (SBL) approach. SBL is shown to be a correlation-aware method and, for the underlying problem, a grid-based technique for recovering a structured covariance matrix of the measurements.
- Categories:
 36 Views
36 Views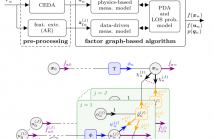
- Read more about A Neural-enhanced Factor Graph-based Algorithm for Robust Positioning in Obstructed LOS Situations
- Log in to post comments
This paper presents a neural-enhanced probabilistic model and corresponding factor graph-based sum-product algorithm for robust localization and tracking in multipath-prone environments. The introduced hybrid probabilistic model consists of physics-based and data-driven measurement models capturing the information contained in both, the line-of-sight (LOS) component as well as in multipath components (NLOS components).
ICASSP2024Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 20 Views
20 Views
- Read more about JOINTLY LEARNING SELECTION MATRICES FOR TRANSMITTERS, RECEIVERS AND FOURIER COEFFICIENTS IN MULTICHANNEL IMAGING
- Log in to post comments
Strategic subsampling has become a focal point due to its effectiveness in compressing data, particularly in the Full Matrix Capture (FMC) approach in ultrasonic imaging. This paper introduces the Joint Deep Probabilistic Subsampling (J-DPS) method, which aims to learn optimal selection matrices simultaneously for transmitters, receivers, and Fourier coefficients. This task-based algorithm is realized by introducing a specialized measurement model and integrating a customized Complex Learned FISTA (CL-FISTA) network.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about A SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING APPROACH FOR DETECTING NON-PSYCHOTIC RELAPSES USING WEARABLE-BASED DIGITAL PHENOTYPING
- Log in to post comments
We present MagCIL's approach for the 1st track of the "2nd e-Prevention challenge: Psychotic and Non-Psychotic Relapse Detection using Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping". First we present our approach for preprocessing and extracting features from the wearable's raw data. We then propose a Transformer model for learning self-supervised representations from augmented features, trained on data from non-relapse days from each of the 9 patients of the challenge. We adopt two unsupervised methods for detecting relapse days as outliers.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views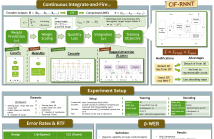
- Read more about CIF-RNNT: Streaming ASR via Acoustic Word Embeddings with Continuous Integrate-and-Fire and RNN-Transducers
- Log in to post comments
This paper introduces CIF-RNNT, a model that incorporates Continuous Integrate-and-Fire into RNN-Transducers (RNNTs) for streaming ASR via acoustic word embeddings (AWEs). CIF can dynamically compress long sequences into shorter ones, while RNNTs can produce multiple symbols given an input vector. We demonstrate that our model can not only streamingly segment acoustic information and produce AWEs, but also recover the represented word using a fixed set of output tokens with a shorter decoding time.
- Categories:
 93 Views
93 Views
- Read more about 3D CBCT CHALLENGE 2024: IMPROVED CONE BEAM CT RECONSTRUCTION USING SWINIR-BASED SINOGRAM AND IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we present our approach to the 3D CBCT Challenge 2024, a part of ICASSP SP Grand Challenges 2024. Improvement in Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) reconstruction has been achieved by integrating Swin Image Restoration (SwinIR) based sinogram and image enhancement modules. The proposed methodology uses Nesterov Accelerated Gradient Descent (NAG) to solve the least squares (NAG-LS) problem in CT image reconstruction.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views