- Bayesian learning; Bayesian signal processing (MLR-BAYL)
- Bounds on performance (MLR-PERF)
- Applications in Systems Biology (MLR-SYSB)
- Applications in Music and Audio Processing (MLR-MUSI)
- Applications in Data Fusion (MLR-FUSI)
- Cognitive information processing (MLR-COGP)
- Distributed and Cooperative Learning (MLR-DIST)
- Learning theory and algorithms (MLR-LEAR)
- Neural network learning (MLR-NNLR)
- Information-theoretic learning (MLR-INFO)
- Independent component analysis (MLR-ICAN)
- Graphical and kernel methods (MLR-GRKN)
- Other applications of machine learning (MLR-APPL)
- Pattern recognition and classification (MLR-PATT)
- Source separation (MLR-SSEP)
- Sequential learning; sequential decision methods (MLR-SLER)
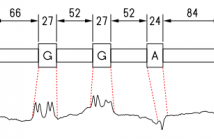
- Read more about Pattern Localization in Time Series through Signal-To-Model Alignment in Latent Space
- Log in to post comments
In this paper, we study the problem of locating a predefined sequence of patterns in a time series. In particular, the studied scenario assumes a theoretical model is available that contains the expected locations of the patterns. This problem is found in several contexts, and it is commonly solved by first synthesizing a time series from the model, and then aligning it to the true time series through dynamic time warping. We propose a technique that increases the similarity of both time series before aligning them, by mapping them into a latent correlation space.
- Categories:
 34 Views
34 ViewsMatrix completion refers to the recovery of a low‐rank matrix from only a subset of its possibly noisy entries, and has a variety of important applications such as collaborative filtering, image inpainting and restoration, system identification, node localization and genotype imputation. It is because many real-world signals can be approximated by a matrix whose rank is much smaller than the row and column numbers. Most techniques for matrix completion in the literature assume Gaussian noise and thus they are not robust to outliers.
- Categories:
 443 Views
443 Views- Read more about ASSESSING THE PROGNOSTIC IMPACT OF 3D CT IMAGE TUMOUR RIND TEXTURE FEATURES ON LUNG CANCER SURVIVAL MODELLING
- Log in to post comments
In this paper we examine a technique for developing prognostic image characteristics, termed radiomics, for non-small cell lung cancer based on a tumour edge region-based analysis. Texture features were extracted from the rind of the tumour in a publicly available 3D CT data set to predict two-year survival. The derived models were compared against the previous methods of training radiomic signatures that are descriptive of the whole tumour volume. Radiomic features derived solely from regions external, but neighbouring, the tumour were shown to also have prognostic value.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Adaptive Basis Selection for Compressed Sensing in Robotic Tactile Skins
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 4 Views
4 Views
- Categories:
 13 Views
13 Views- Read more about COMBINATORIAL MULTI-ARMED BANDIT PROBLEM WITH PROBABILISTICALLY TRIGGERED ARMS: A CASE WITH BOUNDED REGRET
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views- Read more about Generating Forbidden Region Virtual Fixtures By Classification of Movement Intention Based on Event-Related Desynchronization
- Log in to post comments
The development of children’s cognitive and perceptual skills depends heavily on object exploration and manipulative experiences. New types of robotic assistive technologies that enable children with disabilities to interact with their environment, which prove to be beneficial for their cognitive and perceptual skills development, have emerged in recent years. In this study, a human-robot interface that uses Event-Related Desynchronization (ERD) brain response during movement was developed.
- Categories:
 11 Views
11 Views- Read more about Poster for GlobalSIP 2017 Paper #1180: The Impact of Sports Sentiment on Stock Returns: A Case Study from Professional Sports Leagues
- Log in to post comments
poster.pdf
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about Sparse Modeling in Image Processing and Deep Learning (Keynote Talk)
- Log in to post comments
Sparse approximation is a well-established theory, with a profound impact on the fields of signal and image processing. In this talk we start by presenting this model and its features, and then turn to describe two special cases of it – the convolutional sparse coding (CSC) and its multi-layered version (ML-CSC). Amazingly, as we will carefully show, ML-CSC provides a solid theoretical foundation to … deep-learning.
- Categories:
 348 Views
348 Views