- Bayesian learning; Bayesian signal processing (MLR-BAYL)
- Bounds on performance (MLR-PERF)
- Applications in Systems Biology (MLR-SYSB)
- Applications in Music and Audio Processing (MLR-MUSI)
- Applications in Data Fusion (MLR-FUSI)
- Cognitive information processing (MLR-COGP)
- Distributed and Cooperative Learning (MLR-DIST)
- Learning theory and algorithms (MLR-LEAR)
- Neural network learning (MLR-NNLR)
- Information-theoretic learning (MLR-INFO)
- Independent component analysis (MLR-ICAN)
- Graphical and kernel methods (MLR-GRKN)
- Other applications of machine learning (MLR-APPL)
- Pattern recognition and classification (MLR-PATT)
- Source separation (MLR-SSEP)
- Sequential learning; sequential decision methods (MLR-SLER)

- Read more about Supplemental for EVENT-BASED EGOCENTRIC HUMAN POSE ESTIMATION IN DYNAMIC ENVIRONMENT
- Log in to post comments
Supplemental for Event-based Egocentric Human Pose Estimation in Dynamic Environment
- Categories:
 134 Views
134 Views
- Read more about supplementary_1502_icip_2025
- Log in to post comments
Machine Unlearning addresses the challenge of efficiently removing the influence of specific data from ML models, in response to data privacy laws and user requests for data deletion. Beyond simply excluding data from the training set, unlearning requires erasing its effects on the model parameters. We present a novel unlearning framework Unlogit, that uses sensitivity-weighted adjustments in model logits to forget selected data.
- Categories:
 29 Views
29 Views
- Read more about PPREDICTING UNCANNY PERCEPTION IN VIRTUAL HUMANS FACES THROUGH IMAGE FEATURES
- Log in to post comments
The perception of strangeness or discomfort in virtual humans, as described by the Uncanny Valley (UV) theory, plays a critical role in shaping users’ interactions with technology. Understanding this phenomenon is essential to reduce its impact during the design and animation of virtual humans. While numerous studies have explored the subjective dimensions of the UV effect, focusing on human perception, our research proposes a novel methodology to investigate this phenomenon by correlating objective image character istics of virtual humans with users’ subjective perceptions of discomfort.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views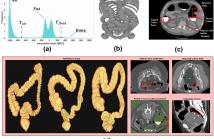
- Read more about Accurate colon segmentation using 2D convolutional neural networks with 3D contextual information
- Log in to post comments
This study introduces an innovative framework for accurate colon segmentation in abdomen CT scans, addressing the unique challenges of this task. Our architecture enhances well-established 2D segmentation models by incorporating 3D contextual information through a novel method that generates an attention map for a given slice by considering its neighboring slices. This approach achieves effective colon segmentation without complex 3D convolutional neural networks (CNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks by combining 2D CNNs.
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Giraffe: A Genetic Programming Algorithm To Build Deep Learning Ensembles For Ecg Arrhythmia Classification
- Log in to post comments
Cardiovascular diseases remain one of the leading causes of death worldwide. Therefore, developing and validating automated tools to help identify high-risk patients are of paramount clinical utility. In this article, we tackle this task and introduce a genetic programming algorithm (called GIRAFFE) to build (deep) machine learning classification ensembles for arrhythmia classification from two-dimensional images of 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG) tracings.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views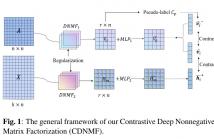
- Read more about [Poster] Contrastive Deep Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Community Detection
- Log in to post comments
Recently, nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely adopted for community detection, because of its better interpretability. However, the existing NMF-based methods have the following three problems: 1) they directly transform the original network into community membership space, so it is difficult for them to capture the hierarchical information; 2) they often only pay attention to the topology of the network and ignore its node attributes; 3) it is hard for them to learn the global structure information necessary for community detection.
- Categories:
 69 Views
69 Views
- Read more about [Poster] Contrastive Deep Nonnegative Matrix Factorization For Community Detection
- Log in to post comments
Recently, nonnegative matrix factorization (NMF) has been widely adopted for community detection, because of its better interpretability. However, the existing NMF-based methods have the following three problems: 1) they directly transform the original network into community membership space, so it is difficult for them to capture the hierarchical information; 2) they often only pay attention to the topology of the network and ignore its node attributes; 3) it is hard for them to learn the global structure information necessary for community detection.
ICASSP2024-Poster.pdf
- Categories:
 61 Views
61 Views
- Read more about Recent Advances in Scalable Energy-Efficient and Trustworthy Spiking Neural Networks: From Algorithms to Technology
- Log in to post comments
Neuromorphic computing and, in particular, spiking neural networks (SNNs) have become an attractive alternative to deep neural networks for a broad range of signal processing applications, processing static and/or temporal inputs from different sensory modalities, including audio and vision sensors. In this paper, we start with a description of recent advances in algorithmic and optimization innovations to efficiently train and scale low-latency, and energy-efficient spiking neural networks (SNNs) for complex machine learning applications.
- Categories:
 39 Views
39 Views
- Read more about Training Ultra-Low-Latency Spiking Neural Networks from Scratch
- Log in to post comments
Spiking Neural networks (SNN) have emerged as an attractive spatio-temporal computing paradigm for a wide range of low-power vision tasks. However, state-of-the-art (SOTA) SNN models either incur multiple time steps which hinder their deployment in real-time use cases or increase the training complexity significantly. To mitigate this concern, we present a training framework (from scratch) for SNNs with ultra-low (down to 1) time steps that leverages the Hoyer regularizer. We calculate the threshold for each BANN layer as the Hoyer extremum of a clipped version of its activation map.
- Categories:
 66 Views
66 Views- Read more about REGULARIZED CONDITIONAL ALIGNMENT FOR MULTI-DOMAIN TEXT CLASSIFICATION
- Log in to post comments
The most successful multi-domain text classification (MDTC) approaches employ the shared-private paradigm to facilitate the enhancement of domain-invariant features through domain-specific attributes. Additionally, they employ adversarial training to align marginal feature distributions. Nevertheless, these methodologies encounter two primary challenges: (1) Neglecting class-aware information during adversarial alignment poses a risk of misalignment; (2) The limited availability of labeled data across multiple domains fails to ensure adequate discriminative capacity for the model.
- Categories:
 16 Views
16 Views