- Bayesian learning; Bayesian signal processing (MLR-BAYL)
- Bounds on performance (MLR-PERF)
- Applications in Systems Biology (MLR-SYSB)
- Applications in Music and Audio Processing (MLR-MUSI)
- Applications in Data Fusion (MLR-FUSI)
- Cognitive information processing (MLR-COGP)
- Distributed and Cooperative Learning (MLR-DIST)
- Learning theory and algorithms (MLR-LEAR)
- Neural network learning (MLR-NNLR)
- Information-theoretic learning (MLR-INFO)
- Independent component analysis (MLR-ICAN)
- Graphical and kernel methods (MLR-GRKN)
- Other applications of machine learning (MLR-APPL)
- Pattern recognition and classification (MLR-PATT)
- Source separation (MLR-SSEP)
- Sequential learning; sequential decision methods (MLR-SLER)

- Read more about Generalized Multi-Source Inference for Text Conditioned Music Diffusion Models
- Log in to post comments
Multi-Source Diffusion Models (MSDM) allow for compositional musical generation tasks: generating a set of coherent sources, creating accompaniments, and performing source separation. Despite their versatility, they require estimating the joint distribution over the sources, necessitating pre-separated musical data, which is rarely available, and fixing the number and type of sources at training time. This paper generalizes MSDM to arbitrary time-domain diffusion models conditioned on text embeddings.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views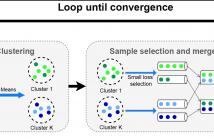
- Read more about Learning with Non-Uniform Label Noise: A Cluster-Dependent Weakly Supervised Approach
- Log in to post comments
Learning with noisy labels is a challenging task in machine learning.
Furthermore in reality, label noise can be highly non-uniform
in feature space, e.g. with higher error rate for more difficult samples.
Some recent works consider instance-dependent label noise
but they require additional information such as some cleanly labeled
data and confidence scores, which are usually unavailable or costly
to obtain. In this paper, we consider learning with non-uniform label
noise that requires no such additional information. Inspired by
poster-3508.pdf
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views
- Read more about Differential DSP Vocoder - ICASSP 2024
- Log in to post comments
Neural vocoders model the raw audio waveform and synthesize highquality audio, but even the highly efficient ones, like MB-MelGAN
and LPCNet, fail to run real-time on a low-end device like a smartglass. A pure digital signal processing (DSP) based vocoder can
be implemented via lightweight fast Fourier transforms (FFT), and
therefore, is a magnitude faster than any neural vocoder. A DSP
vocoder often gets a lower audio quality due to consuming oversmoothed acoustic model predictions of approximate representations
- Categories:
 50 Views
50 Views- Read more about TEN-GUARD: TENSOR DECOMPOSITION FOR BACKDOOR ATTACK DETECTION IN DEEP NEURAL NETWORKS
- Log in to post comments
As deep neural networks and the datasets used to train them get larger, the default approach to integrating them into re-
search and commercial projects is to download a pre-trained model and fine tune it. But these models can have uncertain
provenance, opening up the possibility that they embed hidden malicious behavior such as trojans or backdoors, where
small changes to an input (triggers) can cause the model toproduce incorrect outputs (e.g., to misclassify). This paper
- Categories:
 30 Views
30 Views
- Read more about Personalised Anomaly Detectors and Prototypical Representations for Relapse Detection from Wearable-Based Digital Phenotyping
- Log in to post comments
We describe our contribution to the 2nd e-Prevention challenge, which focuses on the unsupervised non-psychotic (Track 1) and psychotic (Track 2) relapse detection using wearable-based digital phenotyping. We exploit the measurements gathered from the gyroscope, the accelerometer, and the heart rate-related sensors embedded in a smartwatch. We also include the available sleep information in our experiments. Four dedicated autoencoders are trained to learn embedded representations from each one of the considered modalities.
- Categories:
 21 Views
21 Views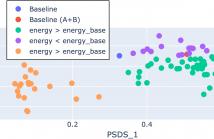
- Read more about Performance And Energy Balance: A Comprehensive Study Of State-Of-The-Art Sound Event Detection Systems - Poster
- 2 comments
- Log in to post comments
In recent years, deep learning systems have shown a concerning trend toward increased complexity and higher energy consumption. As researchers in this domain and organizers of one of the Detection and Classification of Acoustic Scenes and Events challenges task, we recognize the importance of addressing the environmental impact of data-driven SED systems. In this paper, we propose an analysis focused on SED systems based on the challenge submissions. This includes a comparison across the past two years and a detailed analysis of this year’s SED systems.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views
- Read more about Search for gravitational wave probes - A self-supervised learning for pulsars based on signal contexts
- Log in to post comments
The recent successful detection of gravitational waves (GWs) at nanohertz based on pulsar timing arrays has underscored the growing signiffcance of searching for new pulsars, which serve as valuable probes for GWs. However, one of the challenges in this endeavor is the lack of labeled data, which can lead to overfftting and poor generalization in supervised deep neural networks. In this paper, we propose a self-supervised pretext task based on signal con-texts to obtain discriminative radio signal representation.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about Noise-Disentangled Graph Contrastive Learning via Low-Rank and Sparse Subspace Decomposition
- Log in to post comments
Graph contrastive learning aims to learn a representative model by maximizing the agreement between different views of the same graph. Existing studies usually allow multifarious noise in data augmentation, and suffer from trivial and inconsistent generation of graph views. Moreover, they mostly impose contrastive constraints on pairwise representations, limiting the structural correlations among multiple nodes. Both problems may hinder graph contrastive learning, leading to suboptimal node representations.
- Categories:
 33 Views
33 Views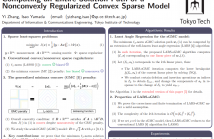
- Read more about Computing an Entire Solution Path of a Nonconvexly Regularized Convex Sparse Model
- Log in to post comments
The generalized minimax concave (GMC) penalty is a nonconvex sparse regularizer which can preserve the overall-convexity of the sparse least squares problem. In this paper, we study the solution path of a special but important instance of the GMC model termed the scaled GMC (sGMC) model. We show that despite the nonconvexity of the regularizer, there exists a solution path of the sGMC model which is piecewise linear as a function of the regularization parameter, and we propose an efficient algorithm for computing a solution path of this type.
- Categories:
 43 Views
43 Views
- Read more about SweepMM: A High-Quality Multimodal Dataset For Sweeping Robots In Home Scenarios For Vision-Language Model
- Log in to post comments
The X-ray security inspection aims to identify any restricted items to protect public safety. Due to the lack of focus on unsupervised learning in this field, using pre-trained models on natural images leads to suboptimal results in downstream tasks. Previous works would lose the relative positional relationships during the pre-training process, which is detrimental for X-ray images that lack texture and rely on shape. In this paper, we propose the jigsaw style MAE (J-MAE) to preserve the relative position information by shuffling the position encoding of visible patches.
- Categories:
 47 Views
47 Views