- Bayesian learning; Bayesian signal processing (MLR-BAYL)
- Bounds on performance (MLR-PERF)
- Applications in Systems Biology (MLR-SYSB)
- Applications in Music and Audio Processing (MLR-MUSI)
- Applications in Data Fusion (MLR-FUSI)
- Cognitive information processing (MLR-COGP)
- Distributed and Cooperative Learning (MLR-DIST)
- Learning theory and algorithms (MLR-LEAR)
- Neural network learning (MLR-NNLR)
- Information-theoretic learning (MLR-INFO)
- Independent component analysis (MLR-ICAN)
- Graphical and kernel methods (MLR-GRKN)
- Other applications of machine learning (MLR-APPL)
- Pattern recognition and classification (MLR-PATT)
- Source separation (MLR-SSEP)
- Sequential learning; sequential decision methods (MLR-SLER)

- Read more about MTAF: SHOPPING GUIDE MICRO-VIDEOS POPULARITY PREDICTION USING MULTIMODAL AND TEMPORAL ATTENTION FUSION APPROACH
- Log in to post comments
Predicting the popularity of shopping guide micro-videos incorporating merchandise is crucial for online advertising. What are the significant factors affecting the popularity of the micro-video? How to extract and effectively fuse multiple modalities for the micro-video popularity prediction? This is a question that needs to be urgently answered to better provide insights for advertisers. In this paper, we propose a Multimodal and Temporal Attention Fusion (MTAF) framework to represent and combine multi-modal features.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views
- Read more about DENOISING-GUIDED DEEP REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR SOCIAL RECOMMENDATION
- Log in to post comments
Social recommendation (SR) aims to enhance the performance of recommendations by incorporating social information. However, such information is not always reliable, e.g., some of the friends may share similar preferences with the user on a specific item, while others may be irrelevant to this item due to domain differences. Therefore, modeling all of the user's social relationships without considering the relevance of friends will introduce noises to the social context.
DRL4So.pptx
- Categories:
 10 Views
10 Views
- Read more about DENOISING-ORIENTED DEEP HIERARCHICAL REINFORCEMENT LEARNING FOR NEXT-BASKET RECOMMENDATION
- Log in to post comments
Next basket recommendation aims to provide users a basket of items on the next visit by considering the sequence of their historical baskets. However, since a user's purchase interests vary over time, historical baskets often contain many irrelevant items to his/her next choices. Therefore, it is necessary to denoise the sequence of historical baskets and reserve the indeed relevant items to enhance the recommendation performance.
HRL4Ba.pptx
- Categories:
 15 Views
15 Views
- Read more about Test-Time Detection of Backdoor Triggers for Poisoned Deep Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 6 Views
6 Views
- Read more about "DYNAMIC RESOURCEOPTIMIZATION FORADAPTIVE FEDERATED LEARNING EMPOWERED BY RECONFIGURABLE INTELLIGENT SURFACES" Poster
- Log in to post comments
The aim of this work is to propose a novel dynamic resource allocation strategy for adaptive Federated Learning (FL), in the context of beyond 5G networks endowed with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs). Due to time-varying wireless channel conditions, communication resources (e.g., set of transmitting devices, transmit powers, bits), computation parameters (e.g., CPU cycles at devices and at server) and RISs reflectivity must be optimized in each communication round, in order to strike the best trade-off between power, latency, and performance of the FL task.
- Categories:
 8 Views
8 Views
- Read more about "DYNAMIC RESOURCEOPTIMIZATION FORADAPTIVE FEDERATED LEARNING EMPOWERED BY RECONFIGURABLE INTELLIGENT SURFACES" Slides
- Log in to post comments
The aim of this work is to propose a novel dynamic resource allocation strategy for adaptive Federated Learning (FL), in the context of beyond 5G networks endowed with Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces (RISs). Due to time-varying wireless channel conditions, communication resources (e.g., set of transmitting devices, transmit powers, bits), computation parameters (e.g., CPU cycles at devices and at server) and RISs reflectivity must be optimized in each communication round, in order to strike the best trade-off between power, latency, and performance of the FL task.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views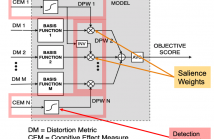
- Read more about A Data-driven Cognitive Salience Model for Objective Perceptual Audio Quality Assessment
- Log in to post comments
Objective audio quality assessment systems often use perceptual models to predict the subjective quality scores of processed signals, as reported in listening tests. Most systems map different metrics of perceived degradation into a single quality score predicting subjective quality. This requires a quality mapping stage that is informed by real listening test data using statistical learning (\iec a data-driven approach) with distortion metrics as input features.
- Categories:
 79 Views
79 Views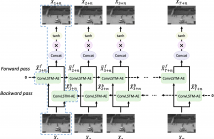
- Read more about Video Anomaly Detection via Prediction Network with Enhanced Spatio-temporal Memory Exchange
- Log in to post comments
Video anomaly detection is a challenging task because most anomalies are scarce and non-deterministic. Many approaches investigate the reconstruction difference between normal and abnormal patterns, but neglect that anomalies do not necessarily correspond to large reconstruction errors. To address this issue, we design a Convolutional LSTM Auto-Encoder prediction framework with enhanced spatio-temporal memory exchange using bi-directionalilty and a higher-order mechanism. The bi-directional structure promotes learning the temporal regularity through forward and backward predictions.
- Categories:
 41 Views
41 Views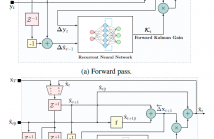
- Read more about RTSNET: DEEP LEARNING AIDED KALMAN SMOOTHING
- Log in to post comments
The smoothing task is the core of many signal processing applications. It deals with the recovery of a sequence of hidden state variables from a sequence of noisy observations in a one-shot manner. In this work we propose RTSNet, a highly efficient model-based and data-driven smoothing algorithm. RTSNet integrates dedicated trainable models into the flow of the classical Rauch-Tung-Striebel (RTS) smoother, and is able to outperform it when operating under model mismatch and non-linearities while retaining its efficiency and interpretability.
- Categories:
 31 Views
31 Views