- Bayesian learning; Bayesian signal processing (MLR-BAYL)
- Bounds on performance (MLR-PERF)
- Applications in Systems Biology (MLR-SYSB)
- Applications in Music and Audio Processing (MLR-MUSI)
- Applications in Data Fusion (MLR-FUSI)
- Cognitive information processing (MLR-COGP)
- Distributed and Cooperative Learning (MLR-DIST)
- Learning theory and algorithms (MLR-LEAR)
- Neural network learning (MLR-NNLR)
- Information-theoretic learning (MLR-INFO)
- Independent component analysis (MLR-ICAN)
- Graphical and kernel methods (MLR-GRKN)
- Other applications of machine learning (MLR-APPL)
- Pattern recognition and classification (MLR-PATT)
- Source separation (MLR-SSEP)
- Sequential learning; sequential decision methods (MLR-SLER)

- Read more about MULTI TASK LEARNING OF DEPTH FROM TELE AND WIDE STEREO IMAGE PAIRS
- 1 comment
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 18 Views
18 Views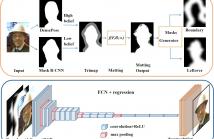
Portrait segmentation is becoming a hot topic nowadays.
In this paper we propose a novel framework to cope with
the high precision requirements that portrait segmentation
demands on boundary area by deep refinement of the
portrait matting. Our approach introduces three novel
techniques. First, a trimap is proposed by fusing information
coming from two well-known techniques for image
segmentation, i.e., Mask R-CNN and DensePose. Second,
an alpha matting algorithm runs over the previous trimap
- Categories:
 167 Views
167 Views
Even though zero padding is usually a staple in convolutional
neural networks to maintain the output size, it is highly suspicious
because it significantly alters the input distribution
around border region. To mitigate this problem, in this paper,
we propose a new padding technique termed as distribution
padding. The goal of the method is to approximately maintain
the statistics of the input border regions. We introduce
two different ways to achieve our goal. In both approaches,
the padded values are derived from the means of the border
- Categories:
 17 Views
17 Views
- Read more about A History-based Stopping Criterion in Recursive Bayesian State Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In dynamic state-space models, the state can be estimated through recursive computation of the posterior distribution of the state given all measurements. In scenarios where active sensing/querying is possible, a hard decision is made when the state posterior achieves a pre-set confidence threshold. This mandate to meet a hard threshold may sometimes unnecessarily require more queries. In application domains where sensing/querying cost is of concern, some potential accuracy may be sacrificed for greater gains in sensing cost.
- Categories:
 9 Views
9 Views
- Read more about A History-based Stopping Criterion in Recursive Bayesian State Estimation
- Log in to post comments
In dynamic state-space models, the state can be estimated through recursive computation of the posterior distribution of the state given all measurements. In scenarios where active sensing/querying is possible, a hard decision is made when the state posterior achieves a pre-set confidence threshold. This mandate to meet a hard threshold may sometimes unnecessarily require more queries. In application domains where sensing/querying cost is of concern, some potential accuracy may be sacrificed for greater gains in sensing cost.
- Categories:
 5 Views
5 Views
- Read more about Estimation of Gaze Region using Two Dimensional Probabilistic Maps Constructed using Convolutional Neural Networks
- Log in to post comments
- Categories:
 26 Views
26 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Speaker Adaptation
- Log in to post comments
We propose a novel adversarial speaker adaptation (ASA) scheme, in which adversarial learning is applied to regularize the distribution of deep hidden features in a speaker-dependent (SD) deep neural network (DNN) acoustic model to be close to that of a fixed speaker-independent (SI) DNN acoustic model during adaptation. An additional discriminator network is introduced to distinguish the deep features generated by the SD model from those produced by the SI model.
- Categories:
 22 Views
22 Views
- Read more about Attentive Adversarial Learning for Domain-Invariant Training
- Log in to post comments
Adversarial domain-invariant training (ADIT) proves to be effective in suppressing the effects of domain variability in acoustic modeling and has led to improved performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR). In ADIT, an auxiliary domain classifier takes in equally-weighted deep features from a deep neural network (DNN) acoustic model and is trained to improve their domain-invariance by optimizing an adversarial loss function.
- Categories:
 24 Views
24 Views
- Read more about Adversarial Speaker Verification
- Log in to post comments
The use of deep networks to extract embeddings for speaker recognition has proven successfully. However, such embeddings are susceptible to performance degradation due to the mismatches among the training, enrollment, and test conditions. In this work, we propose an adversarial speaker verification (ASV) scheme to learn the condition-invariant deep embedding via adversarial multi-task training. In ASV, a speaker classification network and a condition identification network are jointly optimized to minimize the speaker classification loss and simultaneously mini-maximize the condition loss.
- Categories:
 19 Views
19 Views
- Read more about Conditional Teacher-Student Learning
- Log in to post comments
The teacher-student (T/S) learning has been shown to be effective for a variety of problems such as domain adaptation and model compression. One shortcoming of the T/S learning is that a teacher model, not always perfect, sporadically produces wrong guidance in form of posterior probabilities that misleads the student model towards a suboptimal performance.
- Categories:
 52 Views
52 Views